*** FUTURE POSTS WILL ALSO APPEAR AT 'NOW AND NEXT' : https://rolfnorfolk.substack.com
Tuesday, August 21, 2007
REFERENCE SECTION
CARRY TRADE, THE
May 22, 2007: Professor Antal E. Fekete (exchange of letters in The Market Oracle)
CHARITIES
September 30, 2007: World Children's Fund - questions about value for money
CHINA
Sept 25, 2007: China's growing class of advertising and media professionals
Sept 23, 2007: China may use its trade surplus for political/military advantage
Aug 09, 2007: Growing inequality of income in China
Aug 06, 2007: China's near-$1 trillion ownership of US assets
July 18, 2007: James Kynge (my review of his book, "China Shakes The World")
June 19, 2007: James Kynge (article in The Alchemist, November 2004)
May 23, 2007: Intellectual property rights in China
May 21, 2007: China's sovereign wealth fund
CURRENCIES / MONETARY INFLATION
Aug 31, 2007: Maastricht provisions for the European Central Bank, post-EMU
Aug 16, 2007: The weakness of the British pound, in gold terms
Aug 15, 2007: The German DM stronger than the dollar, in gold terms
Aug 14, 2007: The weakness of the dollar compared to gold
Aug 03, 2007: The Euro as a possible international reserve currency
July 31, 2007: Mike Hewitt (article on global money supply in The Market Oracle)
May 28, 2007: Richard Duncan (interview on BusinessInAsia.com)
May 11, 2007: Peter Schiff (my review of his book, "Crash Proof")
May 10, 2007: Michael Panzner (my review of his book, "Financial Armageddon")
DEPOSITOR PROTECTION
Aug 30, 2007: Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (USA)
Aug 23, 2007: Financial Services Compensation Scheme (UK)
DERIVATIVES
July 31, 2007: Richard Bookstaber (interview on Financial Sense, July 21 2007)
ECONOMIC CYCLES & PATTERNS
Sept 16, 2007: Jim Puplava sees crisis in 2009: Peak Oil and other factors
July 27, 2007: Kress cycles
June 28, 2007: Hindenburg omens
May 23, 2007: Olduvai theory
May 16, 2007: the Kondratieff cycle
GLOBALISATION / NEW GROWTH THEORY
Sept 23, 2007: My view that Western economies are facing inflation and recession
Aug 09, 2007: Globalisation and competition from the Far East
July 28, 2007: Thomas Friedman (interview on Yale Global Online, 18 April 2005)
July 28, 2007: Paul Romer (interview on Reason Online, 2001)
July 27, 2007: Wikipedia / Gladys We on New Growth Theory, aka Endogenous Growth Theory July 07, 2007: Thomas Friedman (Edward Leamer's critique)
May 20, 2007: Jim Willie on unemployment caused by globalisation
GOLD
Sept 27, 2007: Marc Faber sees bubbles everywhere, but recommends gold
Sept 25, 2007: More from Frank Veneroso on gold reserves and speculation
Sept 24, 2007: Frank Veneroso thinks speculation has created a bubble in gold
Aug 16, 2007: Mike Hewitt's essay on the global money supply, and gold
Aug 15, 2007: The surreptitious depletion of central bank gold reserves
Aug 07, 2007: The case for owning gold
Aug 02, 2007: The postwar rise and fall of central bank reserves of gold
LEGAL
Aug 24, 2007: Enduring Power of Attorney / Lasting Power of Attorney
MORTGAGES
September 29, 2007: Mortgage lending a key factor in high property costs
PERSONALITY PROFILES
Faber, Marc (Dr)
RISK ASSESSMENT & REDUCTION
Aug 09, 2007: Tips from the Daily Reckoning on defensive investment
June 21, 2007: Nassim Taleb's "Black Swans"
June 15, 2007: Harold Markowitz (inventor of Modern Portfolio Theory)
June 06, 2007: Asset classes
May 11, 2007: Peter Schiff (my review of his book, "Crash Proof")
May 10, 2007: Michael Panzner (my review of his book, "Financial Armageddon")
SOVEREIGN WEALTH FUNDS
Sept 26, 2007: Sovereign wealth funds expected to boost markets - but a threat to Western economies
Sept 22, 2007: Creditor economies switching from bonds to equities
May 21, 2007: China's sovereign wealth fund
STOCKMARKET VOLATILITY
Aug 31, 2007: Robert McHugh's "Dow 9,000" prediction - with updates
Aug 09, 2007: Is the Dow more overvalued than the FTSE?
June 20, 2007: Dow and FTSE past falls
Home
The chef eats his own cooking
Monday, August 20, 2007
More on Faber and Vietnam
In an edition of his GloomBoomDoom report dated May 2003 he remarked, "Vietnam... is developing rapidly and will, in my opinion, with its 80 million very hard-working and thrifty people, overtake Thailand economically within the next ten years or so." For those who may be considering subscribing to his newletters, it's interesting to see an example of his reporting style.
Marc Faber comments on Fed rate cut

Sunday, August 19, 2007
Another bearish opinion
"Anyway, we believe that Friday’s stock market rally (in the US) is a good opportunity to liquidate any existing holdings of stocks."
Doug Casey goes to Argentina
...we're at the end of a 25-year boom. It's gone on more than a full generation now. And I'll tell you how it's going to end: It's going to end with a depression, and not just a depression; not just another Great Depression; it's going to be the Greater Depression...
I think what you ought to have is your citizenship in one country, your bank account in another country, your investments in a third, and live in a fourth. You've got to internationalize yourself...
What am I doing about this? I've been all over the world. I guess I've lived in 12 countries now. And out of 175, I've been to most of them, numerous times actually. What am I doing, where do I want to go, where am I living? Well, in New Zealand.... But... the currency has doubled and the real estate within that currency has doubled at least. So I'm getting out of New Zealand. Where am I going now? I'm going to Argentina...
I wouldn't touch Europe with a ten-foot pole...
...everything in Argentina costs between 10% to 30% of what it costs in North America. That's correct. It's that cheap... So you're getting a massive immigration from rich Europeans that can see the handwriting on the wall and like it down there. And I really like it down there. It's just a great society, great society, great place to hang out, prices are right. I mean this can solve most of your investment problems right there, just by transplanting yourself, if you've got some capital.
This may sound like it's only for the really rich, but I have had perfectly ordinary clients sell up their over-priced ordinary British homes and move permanently to the Far East. For personal reasons, I can't be a globe-trotter, but international relocation is happening on a much bigger scale than London to Provence. For a while, I subscribed to one magazine, "International Living", that looks for bargain locations to spend the rest of your life - Panama appears to be a good one, if you dress conservatively and mind your own business.
So although Mr Casey talks dramatically in a non-Brit sort of way, he is backing his judgement with his considerable money; and ordinary types like ourselves currently have options that we could scarcely have dreamed of before WWII. Whether we will always have such options, is another question.
More on Marc Faber and the bear market
"Excerpts from CNBC-TV18's exclusive interview with Marc Faber:
Q: How do you read the events as they have unfolded in the past fortnight? How do you think this might shape up?
A: Basically as you know, the US market went up until July 16. The Dow peaked out on July 17 above 14,000 and then it started to slide, mainly driven by financial stocks and by what people call a crisis in the subprime lending sector and the CDO and the BS markets. The question obviously is where do we go from here? Is it like 1998, where we dropped first and then recovered strongly towards the end of the year or is it something more serious? I think it's something more serious.
Q: If you had to predict - since your view is bearish, what percentage fall would you expect in emerging market equities over the next foreseeable period?
A: The S&P has a very good chance to decline by 20-30% and the emerging economy stock markets could drop by 40%. That may not mean that the bull market in emerging markets is over for good, because in 1987 we had drops in Taiwan of 50% and then the market went up another four times, so you can have a big correction and still be in the bull market.
But if someone came to me and said what is the upside on the S&P? We had 1,452 where the high was 1,555. I would say the upside and the big resistance in the market is between 1,520 and 1,530 so the upside is limited. But what about the risk?
What I noticed is investors are far more concerned about missing the next leg in the bull market on the upside, than about the risk of losing a lot of money. And I think, gradually this will change and that would mean lower equity prices and also prices of other assets such as commodities can go down substantially and obviously home prices around the world.
Dear Daily Reckoning readers should be aware...this is a downturn that COULD be extremely long and severe."
Marc Faber: India rather than the USA
"If a gun were put to my head and I was asked to choose between two options - putting all my assets into the US or into India - I would choose Indian equities, Indian real estate, and Indian art. The reason behind this choice is partly my strong conviction that US assets will continue to decline relative to assets overseas, and partly because I can see that India may be at the beginning of a lasting economic take-off phase" ...
...From 1978 to February 1990, Marc Faber was the Managing Director of Drexel Burnham Lambert (HK) Ltd. In June 1990, he set up his own business, MARC FABER LIMITED which acts as an investment advisor and fund manager.(Marc Faber - A Simpleton's Guide to Economics and Investment Markets, part II )
By INRnews Correspondent
Dr Faber's comments on Indian urbanisation, the need for new infrastructure, and comparison with China, are also very interesting.
Saturday, August 18, 2007
Weathering the storm
Now that we know the opposition's strategy, what do we do? My guess is, hold cash, wait for further crises of confidence, and buy tangible assets, or assets backed by tangibles, at bargain prices.
That's why I think Buffett and Soros have been so clever in acquiring more rail stock in recent months. Railways are a natural Benjamin Graham choice: mature, income-producing investments. There are big barriers to entry - think of nineteenth-century land speculation and skulduggery, and add-in eco protests, modern politics and the unavailability of coolie labour. Rail has advantages over road, especially as so much freight now is containerised and port-to-city; but from an investor's perspective it is also solidly thing-based.
I think we'll be back to putting money into things we can understand.
Friday, August 17, 2007
Following the markets today
Risk avoidance leads to stronger dollar
These days, cash is a valuable commodity since a liquidity crisis means a lack of cash. The sharpness of recent moves and the lack of liquidity have probably pushed more traders to liquidate positions than to add funds. Flight to safety continues to send the dollar higher against every major currency with the exception of the Japanese Yen as more victims of the subprime and liquidity crisis surface.
There's a possibility of an interest rate reduction:
...the biggest question on everyone’s mind is when the Federal Reserve will cut interest rates. The market is current pricing 75bp of easing by the end of the year. There has also been speculation of an intermeeting rate cut.
But:
Like many central banks around the world, the Fed has been reluctant to lower rates because they feel that the markets need to be punished for their excessive risk appetite. Furthermore, they have said that they need to see market volatility have a “real impact” on the economy.
This, she thinks, is becoming apparent:
With major losses and bankruptcies reported throughout the financial sector, we expect companies to layoff staff left and right. [...] For the people in the “real economy,” their 401ks have taken a harsh beating while their mortgage interest payments are on the rise. It is only a matter of time when we see economics reflect that. The bad news is already pouring in with housing starts hitting a 10 year low and manufacturing activity in the Philadelphia region stagnating. Since the beginning of the year, the weak dollar has provided a big boom to the manufacturing sector. Now that the dollar has strengthened significantly, activity in the manufacturing sector should also begin to slow.
US economy over-dependent on housing sector

Thursday, August 16, 2007
Here is tomorrow's news
 An online newspaper from the Northern Marianas (south-east from Japan), dated Friday, gives some quotes from Peter Schiff, including this startling (and measurable) one:
An online newspaper from the Northern Marianas (south-east from Japan), dated Friday, gives some quotes from Peter Schiff, including this startling (and measurable) one:More on Dow stock valuation
A couple of extracts:
...the stocks in the Standard & Poor's 500 have an average P/E ratio of about 16.8, which by historical standards is normal. Since World War II, the average ratio has been 16.1. During the bubbles of the 1920s and the 1990s, the ratio shot above 30...
Graham and Dodd argued that P/E ratios should compare stock prices to "not less than five years, preferably seven or ten years" of profits...
Based on average profits over the past 10 years, the P/E ratio has been hovering around 27 recently. That's higher than it has been at any other point during the past 130 years, except for the great bubbles of the 1920s and the 1990s. The stock run-up of the 1990s was so big, in other words, that the market may still not have fully worked it off...
In the long term, the stock market will almost certainly continue to be a good investment. But the next few years do seem to depend on a more rickety foundation than Wall Street's soothing words suggest.
A drop from a p/e ratio of 27 down to 16.8 would imply a share price drop of 37%.
Thanks to Michael Panzner for spotting this and putting it onto his Financial Armageddon site.
Weakness of UK M3 relative to gold
World Gold Council June 2007 figures say the UK has 310.3 tonnes of official gold, and Mike Hewitt's table shows UK M3 at $3,532.1 billion. Using the same gold value per kilo as with the other two countries, if the UK's M3 were entirely gold-related, this would imply a price of about $35,4046 per ounce.
From this perspective, although Britain's economy is much smaller than America's, its currency weakness is much closer to America's than to Germany's.
Dow and FTSE lows
More on gold and the money supply
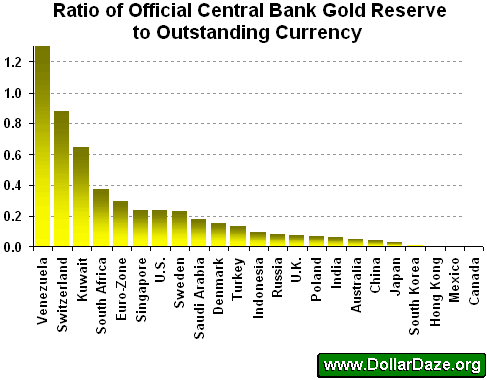 At last, I've found something to help me see currencies in the context of official gold reserves - a brilliantly useful essay by Mike Hewitt in The Market Oracle (July 31).
At last, I've found something to help me see currencies in the context of official gold reserves - a brilliantly useful essay by Mike Hewitt in The Market Oracle (July 31).Sprechen Sie Gibberish?
Let's look at the UK's Daily Mail today, Money Mail section (pages 38-39). The headline is "Storm Warning" - anything from a week to seven years late, depending on your analysis of the underlying trends.
Sub-section: "Will it continue?" Answer: volatility "for the next few months", but "the markets are fundamentally sound in that that they are not over-priced". Yet we've only just heard from Marc Faber, saying that he expects "earnings disappointments" which will show up in the dividends and so alter the p/e ratio for the worse. And on page 66 of the same paper we see disappointments at UBS, Wal-Mart, Home Depot.
The chairman of a large financial advice firm is quoted saying, "You must put this sub-prime mortgage meltdown into perspective. We are talking about £100 billion of losses. [Wait for the punchline.] This sounds like a lot, but it is just one-tenth of the size of the public sector pension liability in this country." Very large, and mostly unfunded, pension liabilities.
Usually, I throw away the money sections of newspapers; I only read them today to see if they'd noticed what was going on. But then I remember that journalists told us for years not to bother with financial advisers, when we could buy our pensions direct from the six-figure wagemen at Equitable Life.
Wednesday, August 15, 2007
Could the German DM be stronger than the US dollar?
I've tried to find equivalent figures for Germany. The latest I can find is from May 1998, when M3 was then estimated at 3,243.70 billion DM. The Deutschmark is pegged at 0.51129 to the Euro, and the US dollar currently buys around 0.73581 Euros. So in dollar terms, German M3 is/was in the region of $1,559 billion.
The World Gold Council's June 2007 figures show Germany holding 3,442.5 tonnes of gold, and there are 31.1034768 grams to the troy ounce, so that's 110,678,945 ounces. If this gold covered all of Germany's M3 at the latter's 1998 estimate, it would imply a gold price of $14,085 per ounce.
Granted that German M3 must now be greater than in 1998, it still suggests that in terms of the ratio of gold to money supply, Germany's currency is around 3 times stronger than the USA's, or one-third as vulnerable in case of hyperinflation.
Silver to ride high?
 Jason Hommel, in this 2 August report on SilverSeek.com, points out that, because of its industrial uses, silver is actually more scarce than gold.
Jason Hommel, in this 2 August report on SilverSeek.com, points out that, because of its industrial uses, silver is actually more scarce than gold.Gold going cold?
This is the problem for doomsters: the 'true' value of gold is most likely to be seen, not in moderately inflationary times, but when faith in paper currency has collapsed and hyperinflation is roaring through the system. It's not something one should wish for, even if it is needed to prove one's theory.
However, there's still the question of how much longer the market can be bought off with these gold stock sales. Eventually there will be nothing left to throw off the back of the troika at the pursuing wolves. And how much has been 'loaned' from stock already?
The article says, "Central banks are the biggest holders of gold, controlling about a fifth of all known supplies." So four-fifths is now in private hands, presumably. You may not feel the time is right to buy gold as a speculation or hedge, but if you had some already, would you sell it now?
Subprime update, plus Dow and gold
Here's iTulip's scathing video on the sub-prime lenders and special pleading from Jim Cramer; and according to this, it was $323 billion pumped into the banking system in 48 hours, not $266 billion.
The Dow closed down 207 points yesterday, anyway. Perhaps you can't pump up a burst balloon.
And gold, which one would think should have an inverse relation to the market, has lost $5 an ounce, too.
Things do look a little concerning.
Gold: a shell game without the pea?
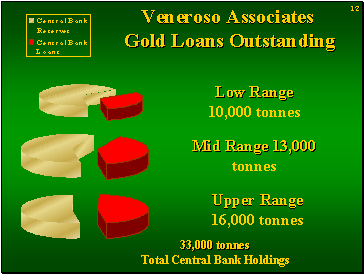 If the gold bugs are right, why hasn't gold rocketed already? Maybe this presentation by Frank Veneroso, dated May 2001, explains it. It makes the case that there is more demand for gold than is officially recognised. This demand cannot be fully satisfied from the declining yields of gold mines, or reusing scrap.
If the gold bugs are right, why hasn't gold rocketed already? Maybe this presentation by Frank Veneroso, dated May 2001, explains it. It makes the case that there is more demand for gold than is officially recognised. This demand cannot be fully satisfied from the declining yields of gold mines, or reusing scrap.Veneroso thinks that central banks have loaned out or sold much more gold than they admit. The World Gold Council states 30,374 tonnes in holdings (June 2007). This is down from the nearly 33,000 in mid-2001 when Veneroso was speaking, and even at that time he estimated 10,000 - 16,000 tonnes out on loan. Much of this will have ended up on ears, fingers and necks.
This theory of market intervention by surreptitious supply, implies that banks must eventually run down their stocks and be unable to continue with this tactic.
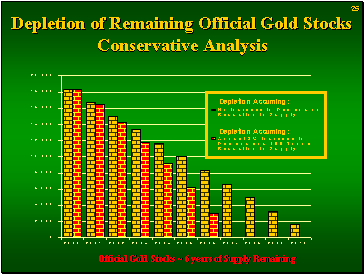 Veneroso speculated: "If the official sector is rational, it knows what will happen to the gold price when this large flow that is depressing the price abates and ultimately ends---the price will go up by a lot. Therefore, some rational central banks will not sell and lend down to the last ounce. Instead they will start to buy. So regardless of what has been happening in the gold market, if our data is correct, then, within a couple of years, whatever the official sector is doing, it will terminate and the gold price will rise."
Veneroso speculated: "If the official sector is rational, it knows what will happen to the gold price when this large flow that is depressing the price abates and ultimately ends---the price will go up by a lot. Therefore, some rational central banks will not sell and lend down to the last ounce. Instead they will start to buy. So regardless of what has been happening in the gold market, if our data is correct, then, within a couple of years, whatever the official sector is doing, it will terminate and the gold price will rise."His prediction was correct: gold has doubled in value since 2005. But as demand continues to grow over time, against a more limited supply, we should see further gold appreciation, which is what Marc Faber has predicted.
But some would go much further - Doug Casey, for instance. If we see the emergence of a very strong currency run by a country or cartel that controls a vital commodity like oil, the inflation in all fiat currencies will be cruelly exposed by contrast. Is it not possible that some might seek to use gold, in conjunction with other commodities, as an economic weapon?
And is it not interesting that the world's second largest gold hoarder, Germany, has disposed of hardly any of its stock in the last 7 years, when the average official reduction has been about 9%? Maybe Germany is taking a longer view and rather than buying gold, is being more discreet and simply not selling it. I wonder how much of its own stock Germany has loaned out?
UPDATE
Please see Monday's essay by James Turk, on Financial Sense. He thinks that the market must ultimately win against the official manipulators.
Tuesday, August 14, 2007
$42 gold: what is the future of the dollar, and central banks?
I think I was right to puzzle over the footnote (in 6-point type!) to the US reserve accounts, which states that gold has been valued at $42 dollars an ounce and that certificates on that basis have been issued to the Federal Reserve.
It looked like dodgy accounting to me, and searching for some further clarification, I found this article in Gold-Eagle.com, dating from 2003. It's by Alex Wallenwein and the style hyperventilates somewhat, but here's some edited highlights:
[France and Germany's] new common currency, the euro, has taken on a characteristic that puts it into direct conflict with the US dollar.
The dollar is a purely debt based currency with an adverse relationship to gold. Gold is the dollar's nemesis. When the gold price goes up, confidence in the dollar decreases and people start selling dollars.. It's usually a sign of impending or prevailing inflation.
The euro, on the other hand, has a "positive" relationship to gold. The European Central Bank, and all the euro member's central banks, value their gold reserves quarterly at actual market prices. That means, as the price of gold goes up, the value of their currency goes up as well, and by signing the "Washington Accord" in 1999 they have announced to the world that the dollar's gold-suppression jig is up.
The dollar is still hamstrung by being tied to an artificial, government-decreed, quasi-official price of gold at the whopping rate of $42.222 per ounce. [See Title 31, United States Code, Section 5117(b).] Obviously, with the market price of gold currently above $330 (i.e. in 2003), that "official price" has nothing to do with the realities of the gold market. It is actually a remnant of the gold standard days when every dollar was immediately convertible into gold on demand, at a stated rate.
Being thus tied down, the US government and banking elite can never afford to let the price of gold float freely according to actual market forces...
This little difference in the valuation of gold makes the euro the undisputed, hands-down future winner of the euro vs dollar conflict... free market forces can never be violated with impunity for a very long time. They always reassert themselves - sooner or later.
The euro was constructed to take advantage of free market forces - especially the free market of gold. The dollar is anchored in a useless, repressive scheme that cannot allow market forces to prevail vis-a-vis gold.
Ergo, the dollar is doomed...
Once it is replaced as the world's reserve currency, the dollar - and with it the United States - will cease to be a world superpower... And all of America's current military might will [be laid to] waste when the international currency reserve dollars return home, causing hyper-inflation and economic havoc...
As the dollar crumbles and loses its control of the price of gold, the yellow metal will soar to heights heretofore unimagined. Nothing will stop it. All economic forces will aid it in its ascent... including... the world's most powerful central banks.
For then, a rising gold price will boost their collective reserves, and therefore their currencies' values, not undermine them as has been the case before the euro's advent.
Gold will be free, and the dollar will be dead: so be careful where you put your money !
The official US price above (still current) is about one-sixteenth what its gold would now fetch on the market. And as I figured late last month, even at open market prices, America's gold reserves only cover around 1.5% of the dollar money supply defined as M3.
In other words, the official price of Treasury bullion makes its total holding worth over 1,000 times less than the amount of money it has in circulation. If ever the world should divorce from the dollar standard, the results could indeed be chaotic.
Now, Iran wants yen from Japan in exchange for oil; the Chinese re-pegged the yuan in 2005 to a "basket of currencies" instead of exclusively to the dollar; the Euro has the potential to be backed by significant national holdings of gold, especially Germany's; an Islamic gold dinar is making its appearance (in Kelantan, Malaysia). I understand that Malaysia is even beginning to entertain the notion of doing away with central banks altogether and taking direct control of its own currency - a financial revolution could be brewing.
Before I get accused yet again of being a gold bug, let me say that I'm not - gold doesn't do anything much except look beautiful, same as our local stray cats. This is not about gold, but about the fiat currencies' potential for real catastrophe, on a Germany-in-1923 scale.
Marc Faber update
A most interesting and informative interview with Marc Faber on Bloomberg TV, last Friday. He thinks we've seen, not a correction, but the start of a bear market. In his opinion, the central banks intervention is inappropriate and will cause inflation. He thinks they "should let the crisis burn through the system, and eliminate some players". The Dow should correct by 20 - 30%; and as hedge funds "de-leverage", i.e. reduce their borrowings, the prices of most assets will drop.
Which one's rich?
 ....................... Who's flying high now?
....................... Who's flying high now? Let's see how we're doing.
Don't get mad
...mortgage underwriting changed beyond recognition between 1998 and 2006, as First American Financial recently reported:
* Adjustable rate mortgages as a percentage of new mortgages rose from 0.7% to 69.5%;
* Negative Amortisation loans - where the principal owed actually increases over time - rose from 0% to 42.2% of the market;
* Interest Only home loans - where the borrower only has to cover the interest due, leaving the principal for repayment sometime in the far future - rose from 0.1% to 35.6%;
* Silent Seconds, issued on the back of outstanding loans to the most vaguely-related people, rose from 0.1% to 38.7%;
* Low Documentation - where the greater the lie, the greater the loan - rose from 57% to 79.8%.
In short, the US mortgage market switched from cautious Fixed-Rate borrowing to head-in-the-sand ARMs...while the underlying debt was left untouched or actually grew larger...as borrowers struggled to meet just the interest alone after fudging the numbers to bag a loan they could never repay.
Most shocking of all, as Robert Rodriguez of First Pacific Advisors has noted, "is that the origination volumes for the last two years, when the most egregious deterioration in underwriting standards occurred, total more than the previous seven years of originations combined."
And this poor-quality debt has been sold to pension funds, very carefully staying just under a crucial limit:
"24% of all the hyper-leveraged assets managed by large hedge funds (US$1 billion or more) internationally, belong to pension funds and endowments," says a June 18 report from Greenwich Associates, as quoted by Paul Gallagher in the Executive Intelligence Review. "This average is just below the 25% limit at which an individual hedge fund, under the [US] Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) as modified in 2006, becomes an investment advisor with fiduciary responsibility for the pension fund doing the investing - something hedge funds obviously do not want to do."
More than that, pension funds have also stumped up one-fifth of the money held in 'hedge funds of funds', the aggregating super-funds run by many large banks. In first-half 2007, around 40% of current flows into the hedge fund industry has come from pension funds. And "as pension fund money is coming in," says Gallagher, "it's allowing 'smart' money to get out."
...Numerous reports, including a new one from Chicago-based Hedge Fund Research, Inc., have shown 'high net-worth individuals' reducing their net hedge fund investments by half, between 2006 and 2007 - investing instead into real property and stocks. They now account for only about 20% of the assets of hedge funds, which were supposedly made for them."
Instead of high-net-worth billionaires, it's now Joe Public left holding this junk, thanks of course to his well-paid retirement fund managers...
Giving control of your money to a financial "expert" might indeed prove the most foolish decision of all.
To me, this is outrageous. I've written earlier about a brokers' meeting I attended in 1999, where a rep from a technology fund burbled enthusiastically about the "super-boom" to come, and how I felt that the smart money was looking to use us to sell their holdings to suckers. And I think the same happened with the Lloyds of London scandal - advisers were encouraged to help their clients get a seat on what they thought was the gravy train, when the insiders knew it was the vinegar bottle. Now it seems we've seen effectively a raid on pension funds.
I sometimes suspect that the money system is not for storing wealth, but for stealing it.
The authorities should be busting the offenders, not bailing them. We should pay off depositors so they can put their savings elsewhere, re-educate naive financial advisers and institutional fund managers, and bankrupt the swindlers.
Here in England, London's Central Criminal Court has a motto above the entrance:
"Defend the Children of the Poor & Punish the Wrongdoer"
If I were an American, I'd be asking questions about justice and the rule of law: does the nation still protect the weak against the strong? Meanwhile, now that you know how the game is played, find a way to win honourably.
 .................... A South Sea Bubble playing card
.................... A South Sea Bubble playing card
Monday, August 13, 2007
Thirty donkeys and a boiled frog
The question is, can this go on indefinitely? Is it like slowly boiling a frog, or will the frog never die? Doomsters are looking for a final cataclysm, but there have been periodic bubbles and busts for a very long time.
Maybe inflation is simply a slow crime, openly and unendingly committed against savers. We worry about interest rates, market crashes, insolvencies and unemployment, and miss the big story because it's so obvious:
The smuggler
Every first of the month the Mullah would cross the border with thirty donkeys with two bales of straw on each. Each time the custom person would ask the Mullah's profession and the Mullah would reply, "I am an honest smuggler."
So each time The Mullah, his donkeys and the bales of straw would be searched from top to toe. Each time the custom folk would not find anything. Next week the Mullah would return without his donkeys or bales of straw.
Years went by and the Mullah prospered in his smuggling profession to the extent that he retired. Many years later the custom person too had retired. As it happened one day the two former adversaries met in a country far from home. The two hugged each other like old buddies and started talking.
After a while the custom person asked the question which had been bugging him over the years, "Mullah, please let me know what were you smuggling all those years ago?"
The mullah thought for a few seconds and finally revealed his open secret, "Donkeys."
From UKSufi.co.uk
I think the ultimate-crash predictions are an expression of the desire for Justice to arrive, like a deus ex machina. Perhaps it's better simply not to be the victim oneself.
Or saddle 'em up for the Gold Rush?
 Illustration from THE GOLD RUSH DIARY OF FRANK McCREARY (1850)
Illustration from THE GOLD RUSH DIARY OF FRANK McCREARY (1850)More old news
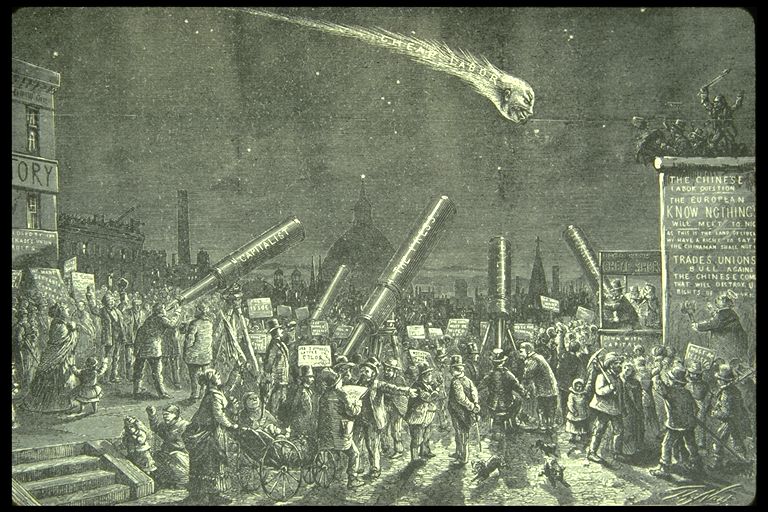 Thomas Nast: "The Comet of Chinese Labour" (1870)
Thomas Nast: "The Comet of Chinese Labour" (1870)The use of cheap foreign labour to undercut unionised American workers and benefit big business, is not new. But as this cartoon shows, it is easy, perhaps politic, to focus on the foreigner, who after all is merely trying to earn a living like the rest of us, and deserves decent treatment, out of common humanity.
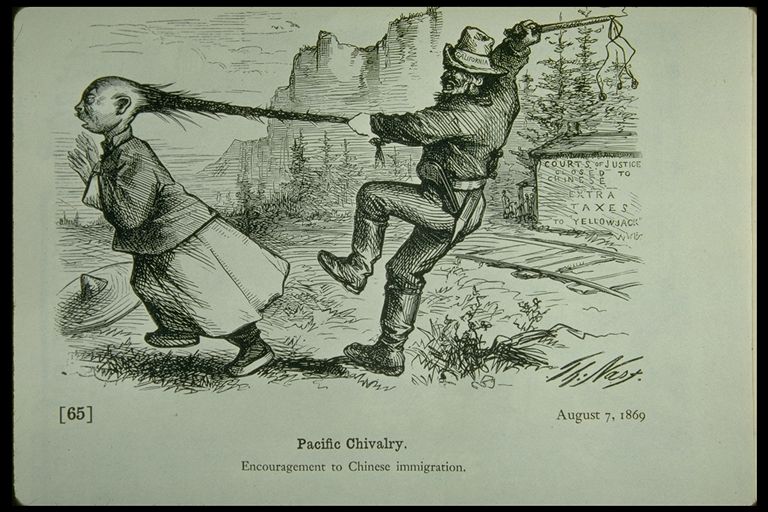 "Pacific Chivalry" (August 7 1869)
"Pacific Chivalry" (August 7 1869)
How do we get a balance between the advantages of international trade, and the obligation of each State to look after its own people?
Sunday, August 12, 2007
Dow predictions revisited
Robert McHugh in Safe Haven predicted on 9 July that the Dow could be heading for 9,000 points, "although if the PPT responds by hyperinflating the money supply, it could be 9,000 in real dollars (gold adjusted), not nominal." The London Gold fix on Friday 6 July 2007 was $661.25 and the Dow at close on that day was 13,649.97, i.e. 20.64 times the gold price per ounce. Dropping to 9,000 as defined would mean a "gold multiple" of 13.61 times, or a 34% relative reduction in share prices.
Perhaps it could happen as a combination of nominal share price reduction, and a devaluation of the dollar.
Not so funny money
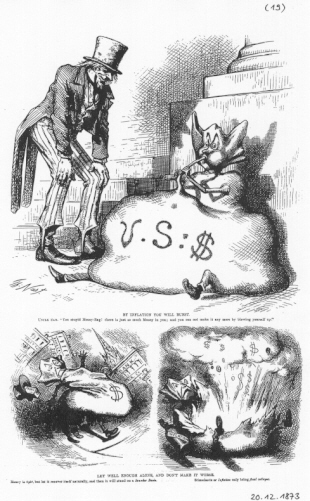 "By inflation you will burst - let well enough alone, and don't make it worse" (Thomas Nast, 20 December 1873)
"By inflation you will burst - let well enough alone, and don't make it worse" (Thomas Nast, 20 December 1873)Captions: (1) UNCLE SAM-"You stupid Money-Bag! there is just so much Money in you; and you can not make it any more by blowing yourself up." (2) Money is tight, but let it recover itself naturally, and then it will stand on a sounder basis. (3) Stimulants or inflation only bring final collapse.
Saturday, August 11, 2007
Doug Casey: sounding grim and clear
At some point there’s going to be a panic out of the dollar. When it happens, it’s likely to be the biggest financial upset since the 1930s. Part of the question is what they’ll panic into. The euro? As I have said many times, if the dollar is an “I owe you nothing,” the euro is a “Who owes you nothing?”...
If an American doesn’t get significant assets outside the U.S. now, it may be impossible in the future. The best thing to do is buy real estate abroad, since it’s currently not reportable, like bank and brokerage accounts, and they can’t very well make you repatriate it...
We’re now experiencing a lot of monetary inflation, which eventually will be reflected in price inflation. What’s really going to tip this over the edge, however, is the rest of the world deciding to get out of dollars. A lot of those $6 trillion abroad are going to come back to the U.S., and real goods are going to be packed up and shipped abroad. Inflation will explode...
Markets are about trade... At some point the Chinese will want payment in something other than dollars. In the meantime the yuan will go higher...
What do I think is likely? Certainly a depression, probably of the inflationary type. But if there are widespread defaults in the mortgage market because of a housing bust, hundreds of billions of dollars worth of buying would disappear, which is deflationary. You could have both things happening at once, in different parts of the economy...
I hate making predictions, but if things continue down this path, I think we could see gold going over $1,000 within the next 12 months, and maybe even before year-end. And then the mania starts for the mining stocks.
Funny money to the rescue
 Stanley Berkeley's "Gordons and Greys to the front", also known as the Stirrup Charge at Waterloo; a deed to stir any man's heart. Apologies for the trivial use.
Stanley Berkeley's "Gordons and Greys to the front", also known as the Stirrup Charge at Waterloo; a deed to stir any man's heart. Apologies for the trivial use.Friday: what looked like a hairy day on the Dow saw a rescue in the last hour of about 80 points. Was it the vast volumes of cash shovelled into the system by central banks, or the fabled Plunge Protection Team (aka Ronald Reagan's Working Group on Financial Markets? If only we all had such understanding bankers.
Friday, August 10, 2007
Could the Dow drop 50%?
It doesn't seem related to average income (American average earnings have grown more slowly than in the UK); if it relates to greater inequality of income, then presumably if the market turns, rich bears will be capable of pushing it down as fast as it rose. And I doubt that American multinationals have exploited subsidiaries in the Far East that much more than British-based multinationals - or have they?
Or is it money invested through the carry trade, borrowing cheaply from Japan? Then maybe it will unwind when Japanese interest rates rise. Is it the benefit of low American interest rates, thanks to huge foreign support for US Treasury securities? That love affair is coming to an end.
Let's do a thought experiment. 1987 seems a reasonable base year for our measurements, since the markets weathered the "Crash" of October and still ended up ahead by the end. From the end of 1986 to close of business this last Wednesday, the FTSE had grown by some 280%. That works out at around 6.7% capital growth compound per annum, for the whole period; add-in dividends and the reasonable investor should be satisfied.
If the Dow had done exactly the same as the FTSE, it would have grown from 1,895.95 to around 7,200. Instead, it closed on Wednesday last at 13,657.86.
Maybe there's still a lot of air in that balloon.
Reading the signs
I have often wondered about chartists - investment analysts who look for patterns in trading to predict future developments. Here's a video posted on YouTube by Inthemoneystocks.com, an outfit set up this year. The report comments on yesterday's dramatic drop in the Dow.
Sometimes I think it's like astrology; but there may be a grain of truth in it. If relevant market information is already known, then (barring catastrophic surprises) some change happens because of the variable mood of the investors and their predictions of each others' behaviour. Perhaps this chart-reading is less a science and more a pragmatic art related to mass psychology and game-playing strategies.
It's an ill wind... Marc Faber cheers up
 As the stockmarkets gyrate, Marc Faber is still optimistic about Asian real estate. Tientip Subhanij, in today's Bangkok Post, says:
As the stockmarkets gyrate, Marc Faber is still optimistic about Asian real estate. Tientip Subhanij, in today's Bangkok Post, says:The optimism over Asian property has been tested in recent months following the volatility in the global equity markets. The woes of the US sub-prime market have already started to shake confidence. Experts have predicted a major crash in US real-estate prices that would trigger defaults and spread the contagion to most emerging markets.
Many with true faith in Asian property, however, dispute any suggestion of an overheated market in the region. Their contention is that the party has just started for regional property, given that prices in many areas have yet to exceed the peaks they achieved before the Asian financial crisis in 1997.
Marc Faber, the well-known author of Tomorrow's Gold: Asia's Age of Discovery, also believes that while stock markets are vulnerable, Asian real estate presents tremendous opportunities. He thinks that most property assets in Asia are still far below their pre-1997 highs.
Thursday, August 09, 2007
Sound counsel
When trends turn negative, it is better to buck them...to head in a different direction. This is particularly so when the bad trends approach their inevitably catastrophic consequences.
That is what we think may be coming soon - with falling asset prices and falling standards of living in America, and probably in most of the other Anglo-Saxon countries. This is not a time to 'go with the flow,' in other words. The flow will not be going where you want to get.
As a practical matter, the course of action that is best in easy times is essential in hard times. Here, we spell it out for you:
First, you should focus on your own private business...or your own source of revenue. (Bonds, rents, retirement fund, dividend yields...whatever.) Make sure it is solid, protected, efficient and productive. Make sure it is something you understand...something you can see with your own eyes, run by people you trust. If you don't really understand it...or if it involves any form of "enhanced leveraged credit"...dump it.
Second, own the property you want to own, not the property you're hoping will go up in price. Begin, of course, with your own house. Is it the house you really want to live in for the next 5, 10, 20 years? Think long-term; the housing slump could easily last 10 years or more. Then, think about the other property you own. Would you still want to own it is if it went down 30% in price? If not, you might want to reconsider.
Third, make sure your savings and investments are diversified out of the dollar. Most experts now expect the buck to stabilise, but you can't be sure. Ten years from now, the dollar could easily be worth only 10% of its value today. Put some money into euro and yen deposits. Put some into gold too.
Fourth, once your finances are secure you can begin to think about speculating. But don't confuse speculating with investing. You speculate for entertainment, not as a serious way to finance your family. Are stock prices going up or down? You can't know. Nor can you know what prices land, commodities, currencies or anything else will sell for in the future. Don't speculate with money you're not prepared to lose.
This all seems pretty sensible to me, especially since the Dow's dropped 300 points.
UPDATE
Dow down 387 at close.
Is the Dow more overvalued than the FTSE?
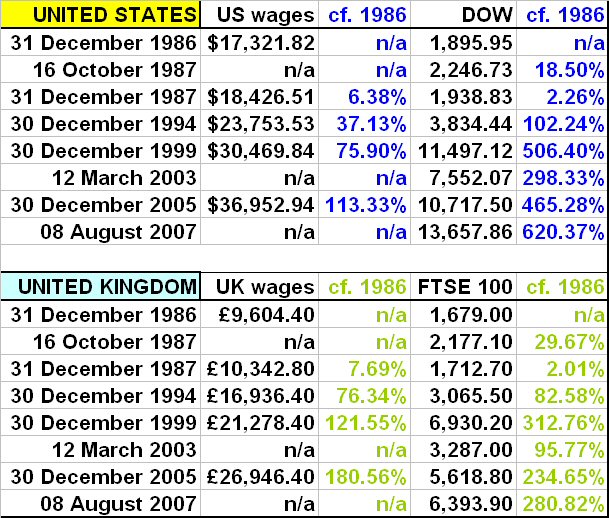 I've compared the growth of the Dow and the FTSE with the increase in national annual average earnings in each country. As you see, the Dow has advanced much more rapidly.
I've compared the growth of the Dow and the FTSE with the increase in national annual average earnings in each country. As you see, the Dow has advanced much more rapidly.UK earnings are calculated as 52* weekly wages. UK stats here, USA stats here. Dow and FTSE stats from the Yahoo! finance website - see sidebar.
Globalisation - a race we can't win
In the sheet below, I compare six countries in terms of nominal per capita GDP (in US dollars equivalent). These have to be reinterpreted in terms of purchasing power parity, i.e. if local prices are lower, you can enjoy the same things for less money. (Nominal and PPP terms are taken from slightly different IMF surveys, but you get the idea.)
The last couple of columns answer the question, "How much income would each national need, to match America's standard of living?"
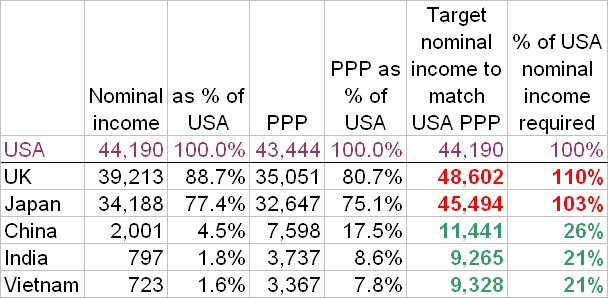 Doubtless there's problems with the methodology - PPP may well change as each country's nominal GDP increases. And it seems clear that the whole world can't live exactly like Americans do today. (It's also interesting to note that pricey, high-tax countries like the UK and Japan can't catch up with the USA without exceeding the latter's per capita GDP.)
Doubtless there's problems with the methodology - PPP may well change as each country's nominal GDP increases. And it seems clear that the whole world can't live exactly like Americans do today. (It's also interesting to note that pricey, high-tax countries like the UK and Japan can't catch up with the USA without exceeding the latter's per capita GDP.)
But on these figures, China could match American living standards, on a quarter the income. So the low-pay trading advantage it enjoys is huge now, and is likely to remain so.
And look at India and Vietnam - they'd only need about one-fifth American per capita income to have the same in PPP terms. In fact, they could out-compete China in labour costs, which is one reason for China to move away from labour-intensive work like trainer-stitching, and towards heavy industry.
So Vietnam undercuts China undercuts America...
And given India's enormous population, its higher proportion of cultivatable land (compared with China), its well-established political and legal institutions, and its many millions of English-language speakers, it may be that India is the economy to watch this century.
IMF per capita GDP figures quoted from Wikipedia here (nominal) and here (PPP).
Subprime worrying Europe
 Looking at the German stock exchange (^GDAXI in the sidebar widget), the market has opened lower. For Reuters comment, see here.
Looking at the German stock exchange (^GDAXI in the sidebar widget), the market has opened lower. For Reuters comment, see here.UPDATE (10.08 a.m.)
The FTSE is looking skittish, too. As Reuters reports: "Richard Hunter, head of UK equities at Hargreaves Lansdown [says], "... as a general rule of thumb, we've certainly been following (Wall) Street on the way down although not necessarily on the way up."
Income inequality rising in China
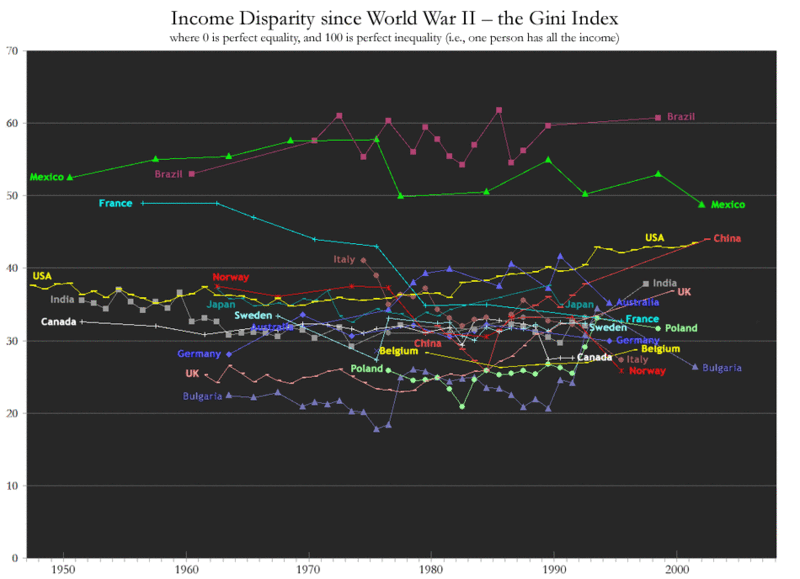 As China industrialises, the difference between rich and poor is rising, as measured by the Gini Index. (The above chart is from the Wikipedia entry. 0 is perfect income equality, 100 means all the income is held by one person. ) The Gini score for China is around the same as for the USA.
As China industrialises, the difference between rich and poor is rising, as measured by the Gini Index. (The above chart is from the Wikipedia entry. 0 is perfect income equality, 100 means all the income is held by one person. ) The Gini score for China is around the same as for the USA.By contrast, China's very rich neighbour Japan has the lowest Gini rating in the Far East, similar to Australia's. It seems possible to achieve prosperity without great inequality.
Speaking of neighbours, see how France's very high score in the 1950s has plunged, whereas the UK's has risen steadily since the 1980s. We in Britain are now significantly more unequal than the French, and far more so than the Belgians and Italians.
Wednesday, August 08, 2007
Gold and other commodities?
Be Fearful, Be Brave - By Monica Day
There's a fundamental rule about investing - you've probably heard it before: Be brave when others are fearful, and fearful when others are brave.
Bill Bonner, editor of Daily Reckoning, opened the Eighth Annual Agora Financial Investment Symposium by suggesting that most people are braver than they've ever been. And that means the rest of us should be very, very afraid.
He's right, of course. Hedge funds are taking in more money than ever…despite the questionable nature of their holdings. Twenty thousand new condos are under construction in Miami…despite the current crisis in the housing sector and the ticking bomb that is subprime lending. The Dow is hitting new highs…with some mainstream commentators calling it the greatest economic boom ever.
Indeed, Bonner agrees it is "great." But more like how the "Great War" and the "Great Depression" were great.
It begs the question - what should you do when you're fearful?
"Nothing," Bonner explains. But that's hard when you have money.
So what exactly constitutes nothing?
If you're a regular reader of these pages, Bonner's answer won't surprise you a bit: Buy gold.
Doug Casey…the Mogambo Guru…and a number of speakers have agreed. Although gold is already up to a 27-year high, it still seems cheap compared with the state of the economy - and the risks the market is facing - right now.
Doug Casey ran through a list of other asset classes and gave his reasons for not wanting his money in them, and he came to this conclusion:
"Where should your money be? GOLD! That's it. Honestly. I've looked at everything and anything - I'll buy anything if the price is right. Gold isn't just going through the roof - it's going through the moon. Mark my words, the gold bull market hasn't even really started…."
And of course, the Mogambo Guru had his own unique way of making a gold recommendation:
"Run out and load up on gold…and in the future when gold prices are astronomical and there's chaos all around you…you'll look around you and notice that you're rich and everyone else is poor and you'll say, wow, that Mogambo dude was right. It's a shame he was such a hateful, detestable little man. And you'll be right…but you'll be rich! So who cares…"
Of course…the "buy gold" line of thinking was not unanimous. Some of the experts and analysts at the Symposium offered worthwhile alternatives to simply buying gold. Natural resource expert Rick Rule was one of them.
Rule believes that you must be brave if you're going to invest in natural resources. Not crazy, mind you. But brave. Meaning you have to be a discriminate investor. You must buy when others are selling, sell when others are buying. This tactic, Rule admits, "is psychologically hard, but functionally easy. And it's the only way to make money consistently in the volatile resource markets."
Byron King, editor of Outstanding Investments, examined investment opportunities among oil and gas stocks. Because the world is no longer awash in oil, King declared, the energy sector - both traditional and alternative - will be awash in great opportunities.
The "cheap oil" days are over, he warned, which means the energy-dependent American lifestyle will become costlier to maintain…maybe much costlier. "We've invented the cheap-energy system that has given us prosperity and freedom," King explained, "now we begin the descent. We'll either have to invent our way out of it, or go back to the way it was before."
He was talking, of course, about our petroleum-based economy… in the face of Peak Oil. Once mocked, denied and ridiculed, the realities of Hubbert's theory are now coming to pass as, one by one, the world's oil fields pass their peak production rates and ease into decline.
If people like Byron King and Bill Bonner are right, the shock of recognition is going to come. But the flip side of this looming societal trauma, says King, is that all kinds of energy companies will make all kinds of money.
Our resident Maniac Trader, Kevin Kerr, also banged the natural resource drum - but to a slightly different beat: Food.
More specifically - how in the world is China going to feed all those people? Even with its one-child policy in place, the population of China is expected to go from 1.3 billion today to 1.49 billion by 2025. But only 11% of China's land is arable farmland. Compare that with 26% in the U.S. to feed a smaller population and you can start to see for yourself: China is in desperate need of a solution.
Plus, it is struggling with other issues. Combine factors such as soil erosion, inadequate water supply, lack of qualified labor for farming, lack of modern farming equipment and methods and extreme weather patterns, and you've got a darn good crisis in the making. But crisis spells opportunity.
A lot of bad things might happen in the world. Some we can foresee, while others will be like the proverbial Black Swan - completely unanticipated. But if you pay attention…and play your hand right…the bad things shouldn't happen to you.
Doug Casey said it best…
"Internationalize yourself. Keep your citizenship in one country, your bank account in another and live in another…treat the world as your oyster."
Tuesday, August 07, 2007
Why gold?
 The Market Oracle yesterday and Gold Seek today both feature an article by Michael Kosares from his own site (USA Gold) on why he thinks you should own gold.
The Market Oracle yesterday and Gold Seek today both feature an article by Michael Kosares from his own site (USA Gold) on why he thinks you should own gold.One reason is the fecklessness of the US Government:
"...the national debt stands at $8.9 trillion - nearly $30,000 for every man, woman and child in the United States. And there appears to be no end in sight to the fiscal madness. The debt clock ticks non-stop at the rate of about $1.3 billion per day.
I should point out that there is a difference between the "deficit" and "additions to the national debt." The deficit often quoted by politicians and the mainstream press is discounted by borrowings from the social security fund - a machination meant to dilute the real budget deficit which is the actual addition to the national debt."
I only knew recently about this business of putting their hands in the social security till and leaving an IOU. That is disturbing, because of the desperation it implies. Wasn't it the financial cost of the First World War that led to the raid on British social security funds and the switch to a rob-Peter-to-pay-Paul system?
Kosares starts his article with two quotes (I've added the sources):
"[U]nder the placid surface there are disturbing trends: huge imbalances, disequilibria, risks -- call them what you will. Altogether the circumstances seem to me as dangerous and intractable as any I can remember, and I can remember quite a lot. What really concerns me is that there seems to be so little willingness or capacity to do much about it. . . We are skating on thin ice." - Paul Volcker, Former Chairman of the Federal Reserve (Washington Post, 10 April 2005)
"[W]e live in a globalized environment and in a country which has enormous fiscal and external deficits. So you have to figure out some way -- which I have not done I might add -- to protect yourself if we should have a real currency problem here." - Robert Rubin, Former Treasury Secretary (interview with Kim Schoenholtz, Citigroup New York, 10 October 2006)
He discusses 6 trends: the US National Debt, the trade deficit, dropping real rates of investment return, derivatives, debt to foreigners, the US dollar's decline.
The conclusion, obviously, is that in times of doubt and distrust, gold will act as a haven for real wealth, as it has done in the past. "Price appreciation... is a sidebar to gold ownership. The main story is gold's asset preservation qualities."