How Britain became a police state
Here is an extract (presentation altered to make visually clearer the catalogue of the State's crimes against liberty) from Philip Pullman's recent article on freedom in the UK - strangely, suspiciously, perhaps tragically and symptomatically, censored from the Internet by The Times:
It is inconceivable to me that a waking nation in the full consciousness of its freedom would have allowed its government to pass such laws as:
the Protection from Harassment Act (1997)
the Crime and Disorder Act (1998)
the Regulation of Investigatory Powers Act (2000)
the Terrorism Act (2000)
the Criminal Justice and Police Act (2001)
the Anti-Terrorism, Crime and Security Act (2001)
the Regulation of Investigatory Powers Extension Act (2002)
the Criminal Justice Act (2003)
the Extradition Act (2003)
the Anti-Social Behaviour Act (2003)
the Domestic Violence, Crime and Victims Act (2004)
the Civil Contingencies Act (2004)
the Prevention of Terrorism Act (2005)
the Inquiries Act (2005)
the Serious Organised Crime and Police Act (2005)
... not to mention a host of pending legislation such as the Identity Cards Bill, the Coroners and Justice Bill, and the Legislative and Regulatory Reform Bill.
For the full article, saved from the memory hole by alert patriots and lovers of liberty, please see here.
By what damning irony is it, that The Times itself should have published this noble extract on June 10, 1788:
THE PROGRESS OF LIBERTY IN ENGLAND
From Mr Pratt’s Poem on Humanity
MARK by what gradual steps Britannia rose;
As the small acorn to a forest grows;
By what variety of adverse fate,
Terrors of war, and anarchies of state,
What direful griefs by foreign fury bred,
Rivers of blood, and mountains of the dead;
She passed advent’rous, e’er her wrongs were o’er,
Complete her triumphs, and confirm’d her pow’r.
When but to look, was treason to the State
And the King’s nod, like thund’ring Jove’s, was fate.
[...]
Thus, in the earliest hour of Britain’s morn,
A Briton’s hate of tyranny was born!
Abhorrence sacred, to repel the hand,
That dares to wrong the charter of the land:
Our sturdy ancestors, tho’ oft subdu’d,
But breach’d from war, and strait the charge renew’d;
Now dres’d as victims, now as pris’ners bound,
The blood of heroes deluging the ground.
In each extreme our brave fore-fathers prove,
Their native courage and their country’s love;
Fierce for hereditary claims they fight,
And ev’n till death maintain a Briton’s right.
Hence rose our liberties, a common cause
To these succeed, their best support, the laws;
Bonds, conflicts, murders, massacres ensu’d,
And many a Saxon, Danish sword embrued
In English blood, and many a Monarch’s life,
And many a Monk’s, submitted to the strife,
E’er Laws were form’d, as now sublime they stand,
The shield, the spear, and buckler of the land.
No wonder they have all but abolished the teaching of English history and literature, as we once knew it.
*** FUTURE POSTS WILL ALSO APPEAR AT 'NOW AND NEXT' : https://rolfnorfolk.substack.com
Showing posts with label UK. Show all posts
Showing posts with label UK. Show all posts
Saturday, February 28, 2009
Wednesday, February 25, 2009
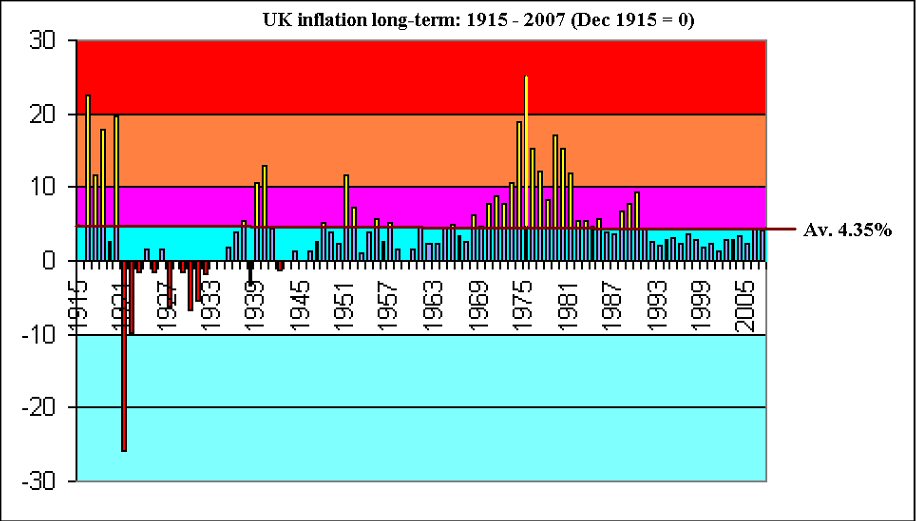
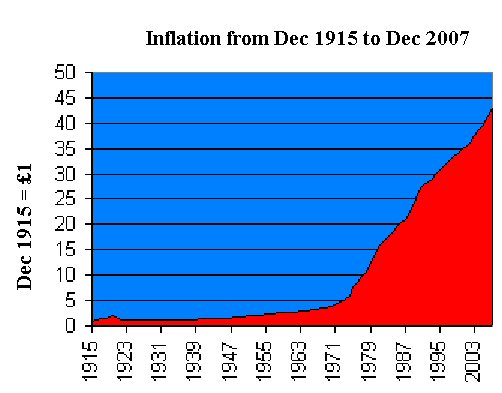
Theft by inflation has begun already
The UK Debt Management Office website shows that a UK Treasury bond offering 5% annual interest is, because of its current traded price, actually yielding 2.522793%.
But the risk of default, almost as high as Italy's government debt and far higher than even the USA's, is (as Jesse quotes) currently priced at 1.63%. (The market currently prices the risk of USA default at 1%.)
So after insuring for risk, 5-year UK sovereign debt earns you less than 0.893%.
Inflation, as measured by the Consumer Price Index*, now runs at 3%. In other words, a "safe" government bond loses you more than 2% a year.
And that's before inflation really gets going.
_____________________________________
*The Retail Price Index is a different measure of inflation, which takes into account mortgage costs. So after recent savage cuts in the bank rate, currently RPI should be negative. But wait until the private capital credit strike leads to higher interest rates, and judge.
But the risk of default, almost as high as Italy's government debt and far higher than even the USA's, is (as Jesse quotes) currently priced at 1.63%. (The market currently prices the risk of USA default at 1%.)
So after insuring for risk, 5-year UK sovereign debt earns you less than 0.893%.
Inflation, as measured by the Consumer Price Index*, now runs at 3%. In other words, a "safe" government bond loses you more than 2% a year.
And that's before inflation really gets going.
_____________________________________
*The Retail Price Index is a different measure of inflation, which takes into account mortgage costs. So after recent savage cuts in the bank rate, currently RPI should be negative. But wait until the private capital credit strike leads to higher interest rates, and judge.
Thursday, February 12, 2009
Symmetry; asymmetry
"China’s January surplus ($39.1b) is roughly the same size as the United States’ December deficit ($39.9b). It is reasonable to think it will roughly match the United States January deficit as well.
The extreme symmetry captures something real. Deficits and surpluses are shrinking globally now that the price of oil is at levels that roughly cover the oil exporters imports. Right now China’s (growing) surplus is clearly the main counterpart to the United States’ (shrinking) deficit" - Brad Setser
"I believe there is a greater than 25pc chance of a departure from the Eurozone given the social and economic behaviours of some countries within it" - John Moulton on the UK and the Euro.
The extreme symmetry captures something real. Deficits and surpluses are shrinking globally now that the price of oil is at levels that roughly cover the oil exporters imports. Right now China’s (growing) surplus is clearly the main counterpart to the United States’ (shrinking) deficit" - Brad Setser
"I believe there is a greater than 25pc chance of a departure from the Eurozone given the social and economic behaviours of some countries within it" - John Moulton on the UK and the Euro.
Tuesday, February 10, 2009
Monday, February 09, 2009
The, er, credit, er, crunch
Thursday, February 05, 2009
Civil liberties in Britain further eroded
Taking a photograph of a public servant, even if it's to record his wrongdoing, is to be illegal. That's if the photograph is 'likely to be useful to a person committing or preparing an act of terrorism'. How could you prove it wasn't?
Nazi comparisons are horrid cliches; yet my mother watched Nazism take hold as she grew up in rural East Prussia. Tyranny advances step by step, and one of its most useful allies is a natural disinclination to believe where it is heading.
Another ally of the tyrant is woolly language used in law - the freedom of the individual is in the precision of the language that grants powers to his incomparably mightier government.
Nazi comparisons are horrid cliches; yet my mother watched Nazism take hold as she grew up in rural East Prussia. Tyranny advances step by step, and one of its most useful allies is a natural disinclination to believe where it is heading.
Another ally of the tyrant is woolly language used in law - the freedom of the individual is in the precision of the language that grants powers to his incomparably mightier government.
Friday, January 23, 2009
Could US interest rates rise?
Brad Setser notes that far from declining in this recession, China's trade surplus is increasing, because although exporting less, it is also importing less. He estimates that China owns $900 billion of US Treasury bonds (and rising), some purchased indirectly via the UK.
However, enormous spending by the US means that it will have to issue a further $900 billion in bonds, and Setser opines, "China isn’t going to double its Treasury holdings in 2009."
If America needs to borrow more than China is willing to lend, the money must come from somewhere else, at a time when it's getting short generally. I have also recently read reports of concerns about the credit rating for US government bonds, which also supports the idea that rates will have to rise to pay for the increased risk of default.
How far will the dollar will be supported by this tendency? At least, in relation to sterling?
The UK is supposed to be an even worse basket case in terms of overall indebtedness, and that may make it politically very difficult to match rates with the US, because it could accelerate the rate of British house repossessions and business bankruptcies, even faster than in the US. So the pound could possibly fall even further against the dollar.
Perhaps Mr Cameron is right to warn that for the UK, the money may run out soon. Then we will have to pay high interest rates after all. And at last, we may be forced to borrow from the IMF and retrench savagely. Back to 1976. And will 1979 return? Cometh the hour, cometh the strong woman?
So, what's the implication of all this for the investor? Sell bonds and buy gold (despite its already high price) now, then reverse the process when high interest rates hit us?
However, enormous spending by the US means that it will have to issue a further $900 billion in bonds, and Setser opines, "China isn’t going to double its Treasury holdings in 2009."
If America needs to borrow more than China is willing to lend, the money must come from somewhere else, at a time when it's getting short generally. I have also recently read reports of concerns about the credit rating for US government bonds, which also supports the idea that rates will have to rise to pay for the increased risk of default.
How far will the dollar will be supported by this tendency? At least, in relation to sterling?
The UK is supposed to be an even worse basket case in terms of overall indebtedness, and that may make it politically very difficult to match rates with the US, because it could accelerate the rate of British house repossessions and business bankruptcies, even faster than in the US. So the pound could possibly fall even further against the dollar.
Perhaps Mr Cameron is right to warn that for the UK, the money may run out soon. Then we will have to pay high interest rates after all. And at last, we may be forced to borrow from the IMF and retrench savagely. Back to 1976. And will 1979 return? Cometh the hour, cometh the strong woman?
So, what's the implication of all this for the investor? Sell bonds and buy gold (despite its already high price) now, then reverse the process when high interest rates hit us?
Thursday, January 08, 2009
Where to turn?
People are starting to run around looking for a haven for wealth. German bond issues partially unsold; US bonds yielding virtually nothing yet at risk of default and dollar devaluation; the UK's economic fundamentals worse than America's (without the advantage of having the world's reserve currency); others saying the PIGS (Portugal, Greece, Italy, Spain) may crash out of the Euro, and that the Euro itself may not see out another ten years.
Marc Faber is predicting that precious metals will outperform equities and bonds; this commentator reckons silver will outperform gold.
Dear me.
Marc Faber is predicting that precious metals will outperform equities and bonds; this commentator reckons silver will outperform gold.
Dear me.
Friday, December 19, 2008
Default
I relayed Jesse's comments on Ecuador's moves to default here on November 28th, and now it's happened. Any big ones coming, do you think?
Saturday, December 06, 2008
And as for the D-word...
The Economist Intelligence Unit democracy index has moved the UK up from 23rd place in 2006 to 21st place in 2008. Of course, this was before the government started nationalising the banks and arresting the Opposition.
Even so, the Civil Liberties strand has fallen in two years from 9.12 to 8.82; and the competition seems to be weakening anyway, as the 2008 report notes:
...following a decades-long global trend in democratisation, the spread of democracy has come to a halt. Comparing the results for 2008 with those from the first edition of the index, which covered 2006, shows that the dominant pattern in the past two years has been stagnation. Although there is no recent trend of outright regression, there are few instances of significant improvement. However, the global financial crisis, resulting in a sharp and possibly protracted recession, could threaten democracy in some parts of the world.
Even so, the Civil Liberties strand has fallen in two years from 9.12 to 8.82; and the competition seems to be weakening anyway, as the 2008 report notes:
...following a decades-long global trend in democratisation, the spread of democracy has come to a halt. Comparing the results for 2008 with those from the first edition of the index, which covered 2006, shows that the dominant pattern in the past two years has been stagnation. Although there is no recent trend of outright regression, there are few instances of significant improvement. However, the global financial crisis, resulting in a sharp and possibly protracted recession, could threaten democracy in some parts of the world.
Saturday, August 30, 2008
Thursday, August 07, 2008
Friday, July 25, 2008
Inflation, deflation, the world economy and freedom
This article by Matthew Beller on the Mises website tries to show how the US government can't "print its way out" of the present crisis.
The Federal Reserve controls the "monetary base" of physical currency and bank deposits, which represent only 15% of the money supply; the rest is bank lending. Currently, the banks are in a fright, so they are reducing credit, on which the economy depends. But if the Federal Reserve increases the monetary base, the banks' ability to multiply their deposits could lead to hyperinflation and the destruction of the dollar altogether. Hence the attempts to maintain confidence in the banking system instead, even if that means expensive financial support.
This isn't enough for the monetarists. They say the lending in the recent boom went on consumer spending, which encouraged producers to make too much of the wrong stuff and so the economy developed in the wrong way. The econo-Puritans say we should accept deflation because, although temporarily painful, it will rebalance the economy for a more sustainable long-term future.
However, nobody likes nasty medicine, so a political question is whether democracies will allow politicians to take timely corrective action. Past history suggests that we'll only vote for the treatment when we're half-dead, and even then, we'll curse the doctor afterwards.
My feeling is that this tendency to delay means that underneath the business cycle is a fatal linear trend, moving wealth and power to less democratic countries. When the world economy recovers, it may be on very different terms: for although (e.g.) China may suffer a setback as the Western consumer reduces spending, Chinese industrial capacity has been growing over recent years - not only the factories and tools, but equally importantly the skills base. At the upturn, the East will be well-placed to cater for reviving demand, while the West struggles to supply appropriately-skilled labour, and tries to buy back some of the industrial materials it had previously exported. And as the East industrialises, it will generate locally a greater proportion of world demand.
I cannot see how we can avoid becoming poorer, on average, than we have been in past decades, even if an elite in our society grows richer and more powerful (a phenomenon associated with more impoverished economies). We cannot rely on high-end production: China will address its quality issues, as Japan did in the 1950s. Nor can we be complacent about intellectual property rights, in a world where might makes right.
But China itself has deep problems - an growing and ageing population; an increasingly unbalanced demographic structure, thanks to attempts to limit family size; pollution; water shortgages; declining quality of farm land. The Chinese leadership faces a long-term challenge in dealing with unsatisfiable domestic expectations, which will tend to make it intransigent in its relations with foreign powers. The East-West contest may become characterized by desperation on both sides.
And so democracy in the West will come under pressure. In difficult times, people are thrown back on a network of social relationships and mutual expectations, but sudden, unreal access of wealth has tempted us to put our faith in the amassing of cash, and/or government intervention, to the detriment of agreed internal social control and support systems. When the system enters its failure phase, which Fischer ("The Great Wave") thinks may be starting, the social threads begin to snap: inflation, crime, family breakdown, war. The reification of the ties that bind us together tempts our government to maintain the social order through externalised means of surveillance and enforcement. Ultimately, the mismanagement of national budgets is a freedom issue.
The Federal Reserve controls the "monetary base" of physical currency and bank deposits, which represent only 15% of the money supply; the rest is bank lending. Currently, the banks are in a fright, so they are reducing credit, on which the economy depends. But if the Federal Reserve increases the monetary base, the banks' ability to multiply their deposits could lead to hyperinflation and the destruction of the dollar altogether. Hence the attempts to maintain confidence in the banking system instead, even if that means expensive financial support.
This isn't enough for the monetarists. They say the lending in the recent boom went on consumer spending, which encouraged producers to make too much of the wrong stuff and so the economy developed in the wrong way. The econo-Puritans say we should accept deflation because, although temporarily painful, it will rebalance the economy for a more sustainable long-term future.
However, nobody likes nasty medicine, so a political question is whether democracies will allow politicians to take timely corrective action. Past history suggests that we'll only vote for the treatment when we're half-dead, and even then, we'll curse the doctor afterwards.
My feeling is that this tendency to delay means that underneath the business cycle is a fatal linear trend, moving wealth and power to less democratic countries. When the world economy recovers, it may be on very different terms: for although (e.g.) China may suffer a setback as the Western consumer reduces spending, Chinese industrial capacity has been growing over recent years - not only the factories and tools, but equally importantly the skills base. At the upturn, the East will be well-placed to cater for reviving demand, while the West struggles to supply appropriately-skilled labour, and tries to buy back some of the industrial materials it had previously exported. And as the East industrialises, it will generate locally a greater proportion of world demand.
I cannot see how we can avoid becoming poorer, on average, than we have been in past decades, even if an elite in our society grows richer and more powerful (a phenomenon associated with more impoverished economies). We cannot rely on high-end production: China will address its quality issues, as Japan did in the 1950s. Nor can we be complacent about intellectual property rights, in a world where might makes right.
But China itself has deep problems - an growing and ageing population; an increasingly unbalanced demographic structure, thanks to attempts to limit family size; pollution; water shortgages; declining quality of farm land. The Chinese leadership faces a long-term challenge in dealing with unsatisfiable domestic expectations, which will tend to make it intransigent in its relations with foreign powers. The East-West contest may become characterized by desperation on both sides.
And so democracy in the West will come under pressure. In difficult times, people are thrown back on a network of social relationships and mutual expectations, but sudden, unreal access of wealth has tempted us to put our faith in the amassing of cash, and/or government intervention, to the detriment of agreed internal social control and support systems. When the system enters its failure phase, which Fischer ("The Great Wave") thinks may be starting, the social threads begin to snap: inflation, crime, family breakdown, war. The reification of the ties that bind us together tempts our government to maintain the social order through externalised means of surveillance and enforcement. Ultimately, the mismanagement of national budgets is a freedom issue.
Wednesday, July 23, 2008
In praise of Patrick O'Flynn
This wide-ranging article by the Daily Express' chief political commentator covers many aspects of the broad crisis that led me to start blogging. My interest is not money per se, but about the fate of our country, and here Patrick O'Flynn unrolls a map of our problems, including:
Spot on. But it's still tucked away on page 12 in yesterday's paper edition, well after Madeleine McCann and Amy Winehouse. This stuff should be hitting the front page all the time, because long after we've forgotten the celeb victims of today, we'll be counting the cost of our government's political and economic negligence and incompetence.
- The rise of the East
- The growing power of foreign authoritarian regimes
- The purchase of British enterprises by foreign sovereign wealth funds, and the consequent export of our future dividend income
- Increasing foreign-held UK public debt (again, more income exported)
- Our vulnerability to energy repricing, and inadequate energy security
- Inflation in food and fuel
- Our unbalanced national budget, what with the cost of unemployment, and rising costs in other social benefits such as the NHS
- Inefficiency in the public sector
- The UK's squandering of its North Sea oil opportunity (cf. Norway's £300 billion investment fund)
- British economic decline, and our deterioriating manufacturing base
Spot on. But it's still tucked away on page 12 in yesterday's paper edition, well after Madeleine McCann and Amy Winehouse. This stuff should be hitting the front page all the time, because long after we've forgotten the celeb victims of today, we'll be counting the cost of our government's political and economic negligence and incompetence.
Wednesday, July 16, 2008
Will the UK/US trade balance influence the dollar value of sterling?
Here's some trade stats for UK/USA. Last year, we imported $6.6 billion more from the US than we exported to them. Last night, the exchange rate for the pound rose above US$2.00. For some time, we seem to have been shadowing the dollar, but do we have an incentive to allow the dollar to fall further against the pound?
Or will we be more influenced by the desire not to devalue the amount we have loaned to the US via Treasury bonds? And then there is the possible extra unemployment that could result from UK goods becoming more expensive in dollar terms.
Any forex experts care to give a view?
UPDATE: Here's the answer, it seems:
Weak jobs data knocks pound vs dollar and euro (Reuters)
UPUPDATE: ...And here's a different answer:
Sterling up versus dollar, banks support (Reuters)
Wouldn't roulette be more honest, somehow? "Manque! Pair! Impair! Passe! Noir! Rouge! Numero 17!"
Or will we be more influenced by the desire not to devalue the amount we have loaned to the US via Treasury bonds? And then there is the possible extra unemployment that could result from UK goods becoming more expensive in dollar terms.
Any forex experts care to give a view?
UPDATE: Here's the answer, it seems:
Weak jobs data knocks pound vs dollar and euro (Reuters)
UPUPDATE: ...And here's a different answer:
Sterling up versus dollar, banks support (Reuters)
Wouldn't roulette be more honest, somehow? "Manque! Pair! Impair! Passe! Noir! Rouge! Numero 17!"
Friday, July 11, 2008
UK the financial "black sheep"
The UK now has the worst fiscal profile of any developed country in the North Atlantic sphere.
Daily Telegraph (htp: Mish)
Daily Telegraph (htp: Mish)
Wednesday, April 02, 2008
Thursday, March 06, 2008
From soup to nuts
Steve Moyer gives a pretty clear (occasionally a bit aerated) potted history of the woeful train of events, over the ten years from the start of the technology stock boom to the popping (and it's only just started) of the real estate bubble.
Nobody had to invest in tech stocks, but we all have to live somewhere. A bubble in housing is really pernicious, because it has implications for almost everyone.
Low interest rates inflated property prices, which led to much larger mortgages. Deflating valuations by raising interest rates would trap many mortgage-holders who have taken on big loans and kept up a good credit history so far.
Therefore, unless the government is willing to deal with the political pain of accelerated mortage defaults, interest rates must now stay low-ish for a long time. So I guess that credit risk will be adjusted not by price, but by access: it will simply get harder to find a willing lender. If there is less lending, then that (it seems to me) is deflationary.
I don't believe that the burden of the monster mortgage will be reduced by rapid general inflation of both wages and prices as in the 70s and 80s. Increased world demand for food and energy will inflate prices, but globalisation means that for many - especially the poorer sort - wages won't keep up. The cost of housing will be a generation-long millstone around the neck.
Inflating the currency won't help. It will reduce the wealth of savers, but if we are importing not only luxuries but (increasingly) necessities, inflated wages will be gobbled up by inflated import prices.
Some may argue that currency debasement will make our exports more competitive. But for a long time now, manufacturing industry has been disappearing like snow in midsummer. Even if our export prices should become more competitive because of foreign exchange rates, domestic productive capacity has shrivelled: whole factories and shipyards have gone abroad, and the related human resources have withered, too. You can't reconstruct the proletariat and their workplaces overnight. Gone are the days when the Midlands engineering worker tinkered with metal in his garden shed, showing his son how to use the tools. Half a mile from where I live, one of the big engineering plants set up by the Birmingham-based Lucas family was taken over first by the Italian Magneti Marelli, then by the Japanese super-corp Denso, and now it's been stripped of its machines and will be demolished to make way for... housing. Goodness know how the mortgages on them will be paid.
I think Karl Denninger is right: the banks must be made to eat some of the debt they fed us. Either they will be ruined, or we shall be.
Nobody had to invest in tech stocks, but we all have to live somewhere. A bubble in housing is really pernicious, because it has implications for almost everyone.
Low interest rates inflated property prices, which led to much larger mortgages. Deflating valuations by raising interest rates would trap many mortgage-holders who have taken on big loans and kept up a good credit history so far.
Therefore, unless the government is willing to deal with the political pain of accelerated mortage defaults, interest rates must now stay low-ish for a long time. So I guess that credit risk will be adjusted not by price, but by access: it will simply get harder to find a willing lender. If there is less lending, then that (it seems to me) is deflationary.
I don't believe that the burden of the monster mortgage will be reduced by rapid general inflation of both wages and prices as in the 70s and 80s. Increased world demand for food and energy will inflate prices, but globalisation means that for many - especially the poorer sort - wages won't keep up. The cost of housing will be a generation-long millstone around the neck.
Inflating the currency won't help. It will reduce the wealth of savers, but if we are importing not only luxuries but (increasingly) necessities, inflated wages will be gobbled up by inflated import prices.
Some may argue that currency debasement will make our exports more competitive. But for a long time now, manufacturing industry has been disappearing like snow in midsummer. Even if our export prices should become more competitive because of foreign exchange rates, domestic productive capacity has shrivelled: whole factories and shipyards have gone abroad, and the related human resources have withered, too. You can't reconstruct the proletariat and their workplaces overnight. Gone are the days when the Midlands engineering worker tinkered with metal in his garden shed, showing his son how to use the tools. Half a mile from where I live, one of the big engineering plants set up by the Birmingham-based Lucas family was taken over first by the Italian Magneti Marelli, then by the Japanese super-corp Denso, and now it's been stripped of its machines and will be demolished to make way for... housing. Goodness know how the mortgages on them will be paid.
I think Karl Denninger is right: the banks must be made to eat some of the debt they fed us. Either they will be ruined, or we shall be.
Tuesday, February 26, 2008
Going down
Another grizzly, this time Captain Hook:
You should know that when banks begin to fail in the States, and they will, things could spiral out of control to the extent controls will to need be placed on both digital and physical movement. Transfers between banks will cease up completely, debts will be called in (so pay them off now), systems from food distribution to medical care will break down, and Martial Law will be the result as the population retaliates. Life will change as you know it.
[...] Japan has never really escaped the credit crunch that gripped their economy back in the 90's after bubblizing the real estate market. That's the tell-tale-sign a bubble economy is on its last legs you know - when master planners need resort to bubblizing the real estate market. Generally it's all down hill after that on a secular (long-term) basis because this is a reflection of not just a turn in the larger credit cycle; but more, and the driver of credit growth in the end, this is the signal demographic constraints have turned negative. [...] It's a simple numbers game, where an aging population is less prone to take on debt.
He considers the possibility of a Japanese-style asset deflation, which gels with my earlier thoughts regarding a generation-long UK property slump.
You should know that when banks begin to fail in the States, and they will, things could spiral out of control to the extent controls will to need be placed on both digital and physical movement. Transfers between banks will cease up completely, debts will be called in (so pay them off now), systems from food distribution to medical care will break down, and Martial Law will be the result as the population retaliates. Life will change as you know it.
[...] Japan has never really escaped the credit crunch that gripped their economy back in the 90's after bubblizing the real estate market. That's the tell-tale-sign a bubble economy is on its last legs you know - when master planners need resort to bubblizing the real estate market. Generally it's all down hill after that on a secular (long-term) basis because this is a reflection of not just a turn in the larger credit cycle; but more, and the driver of credit growth in the end, this is the signal demographic constraints have turned negative. [...] It's a simple numbers game, where an aging population is less prone to take on debt.
He considers the possibility of a Japanese-style asset deflation, which gels with my earlier thoughts regarding a generation-long UK property slump.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)