See our energy expert's latest squib here.
Nothing here should be taken as personal advice, financial or otherwise. No liability is accepted for third-party content, whether incorporated in or linked to this blog; or for unintentional error and inaccuracy. The blog author may have, or intend to change, a personal position in any stock or other kind of investment mentioned.
Wednesday, January 16, 2013
Nick Drew: "Green" initiatives have contradictory effects
See our energy expert's latest squib here.
Nothing here should be taken as personal advice, financial or otherwise. No liability is accepted for third-party content, whether incorporated in or linked to this blog; or for unintentional error and inaccuracy. The blog author may have, or intend to change, a personal position in any stock or other kind of investment mentioned.
Nothing here should be taken as personal advice, financial or otherwise. No liability is accepted for third-party content, whether incorporated in or linked to this blog; or for unintentional error and inaccuracy. The blog author may have, or intend to change, a personal position in any stock or other kind of investment mentioned.
Tuesday, January 15, 2013
The Only Solution Is My Solution
The following Grauniad headline gets my prize for best of 2013 so far:
Rogue geoengineering could 'hijack' world's climate
"Determining causation and quantifying impacts would be a massive challenge" !! Are they reading what they are writing ?
This piece first appeared on Capitalists@Work
Nothing here should be taken as personal advice, financial or otherwise. No liability is accepted for third-party content, whether incorporated in or linked to this blog; or for unintentional error and inaccuracy. The blog author may have, or intend to change, a personal position in any stock or other kind of investment mentioned.
Rogue geoengineering could 'hijack' world's climate
"The deployment of independent, large-scale "geoengineering" techniques aimed at averting dangerous warming warrants more research because it could lead to an international crisis with unpredictable costs to agriculture, infrastructure and global stability, said the Geneva-based WEF in its annual Global Risks report"Haha ! They don't like it up 'em, Captain Mainwaring. But aside from 'independent' not fitting with 'dictated by the green lobby', what exactly is the problem ? Let's turn to the report:
"A long series of ethical, legal and scientific questions quickly arises about countless knock-on effects that might be much more difficult to assess ... Almost any change in weather and climate patterns is likely to create winners and losers, but determining causation and quantifying impacts on any given region or country would be a massive challenge."What, unintended consequences ? Well, b****r me ! That would be like, err, when you subsidise biofuels and discover that entire forests are being felled, and food-stocks diverted, for use as fuel ? Or when you subsidise solar power and find that your electricity grid can't cope ? Or when you implement 'green' policies and find that your CO2 emissions are rising ?
"Determining causation and quantifying impacts would be a massive challenge" !! Are they reading what they are writing ?
This piece first appeared on Capitalists@Work
Nothing here should be taken as personal advice, financial or otherwise. No liability is accepted for third-party content, whether incorporated in or linked to this blog; or for unintentional error and inaccuracy. The blog author may have, or intend to change, a personal position in any stock or other kind of investment mentioned.
Saturday, January 12, 2013
Ancient underground city in Turkey!
Seen on Nourishing Obscurity: a fantastic, multi-level underground city that housed up to 10,000 people in siege times, a thousand years ago. Discovered only in 1963, when a Turkish man demolished an interior wall in his dwelling. Don't miss it!
Part 1
Part 2
Part 1
Part 2
Wednesday, January 09, 2013
Green energy can be a killer
When it comes to ecology, there are debates about evidence, and how reliable it may be.
Michael Crichton's 2004 sci-fi novel "State of Fear", which I read recently, shows how scientific data can be misleading or contradictory. For example, historic air temperature measurements in New York City seem to prove that the atmosphere is heating up; but figures over the same period from an instrument in rural New York State show the opposite. Some of the scientists in the book start with a quasi-religious belief in global warming and bend or discount counter-evidence. By the end of the story I was certainly more skeptical than when I started it, though that doesn't mean I was necessarily persuaded to "cross the floor". There's plenty still to argue about; for example, this internet essay offers a reexamination of some of the science in Crichton's book.
In fact, Crichton himself adds an author's note at the end, in which he gives his view that global warming probably is happening, and that human activity is probably contributing to it. His real point (other than entertainment) is to have us examine evidence more critically, and to watch out for the influence of a scientist's more personal motives - grants for research, career progression, public attention.
There are also debates to be had about competing values.
Most of the world's nations have ratified the 1997 Kyoto Protocol on "greenhouse gas" emissions reduction (in force eight years come next Wednesday). We're trying to do our bit to "save the planet": as part of the UK's 2011 Carbon Plan and 2009 Renewable Energy Strategy the Government has initiated the Renewable Heat Incentive. This encourages the burning of waste as a way of providing heat as well as disposing of rubbish. Sounds good, and there happens to be recently-contructed incinerator only a couple of miles away from me, in south Birmingham.
But it's not purely beneficial, as the readers' letters pages in The Oldie magazine point out. In response to TV personality Johnny Ball's lately-expressed support for incinerators, Michael Ryan of Shrewsbury (January 2013 issue) used ONS data to suggest a link between incinerator emissions and increased infant mortality. In the February issue (just out), Chris Butler of Borough Green in Kent writes in to say that the Public Health Observatory blames atmospheric particulates for 5.6% of mortality in England. (That's not to say that all the particles come from incinerators; nor that we'd live forever if the air was clean. But this London website quotes the same PHO figure and says it's worse in London: 6 - 9% of mortality so attributable.)
Mr Butler makes a second reference in the same letter, this time to the DECC's own July 2012 impact assessment of the Renewable Heat Incentive. This attempts to quantify in monetary terms the pros and cons of (a) doing nothing about incinerators' emissions and (b) introducing stricter rules. If the sums are right, the cost of extra regulation discounted back to today would be £420 million, but the benefits in terms of better health and reduced mortality are estimated at nearly £3 billion. (How are exactly are these figures calculated? What happens if the discount rate used (3.5%) is higher or lower? One can imagine the money-debate rattling on.)
And it can be very hard to apply money to values. How do we price health and life per se, apart from the cost of medical interventions, social security costs for the sick and so on? What counts as the best solution depends so much on what kind of, and the degree to which, "negative externality" is internalized into the calculation, if at all. For example, one of the externalities not assessed in this report is the impact on the ecosystem (see paragraph 33).
And one option is simply not to care at all. Stalin's view on externality was brutally simple: no man, no problem.
Not all particulates are equally hazardous, but none is deemed safe: "the World Health Organisation advise that there is no safe exposure level to P(articulate) M(atter)," says the DECC's report. The danger is not uniform in time, either, e.g. more dioxins are emitted at operational startup and shutdown than in mid-burn.
The damage caused by other pollutants is not yet completely known, and there are many of them: "Incinerator emissions are a major source of fine particulates, of toxic metals and of more than 200 organic chemicals, including known carcinogens, mutagens, and hormone disrupters," says this 2008 report by the British Society for Ecological Medicine. Perhaps the chemtrail conspiracy-hunters should turn their attention from the skies to their local waste tip.
What are the facts, then, and what are the relevant facts, and what values should we use in relation to them? There's so much uncertainty and room for disagreement that the precautionary principle might save us much ill-tempered controversy as well as, possibly, harm to life and health: let's simply make less waste in the first place.
Now to put out two large bags of washed plastic bottles, for tomorrow's binmen.
Nothing here should be taken as personal advice, financial or otherwise. No liability is accepted for third-party content, whether incorporated in or linked to this blog; or for unintentional error and inaccuracy. The blog author may have, or intend to change, a personal position in any stock or other kind of investment mentioned.
Michael Crichton's 2004 sci-fi novel "State of Fear", which I read recently, shows how scientific data can be misleading or contradictory. For example, historic air temperature measurements in New York City seem to prove that the atmosphere is heating up; but figures over the same period from an instrument in rural New York State show the opposite. Some of the scientists in the book start with a quasi-religious belief in global warming and bend or discount counter-evidence. By the end of the story I was certainly more skeptical than when I started it, though that doesn't mean I was necessarily persuaded to "cross the floor". There's plenty still to argue about; for example, this internet essay offers a reexamination of some of the science in Crichton's book.
In fact, Crichton himself adds an author's note at the end, in which he gives his view that global warming probably is happening, and that human activity is probably contributing to it. His real point (other than entertainment) is to have us examine evidence more critically, and to watch out for the influence of a scientist's more personal motives - grants for research, career progression, public attention.
There are also debates to be had about competing values.
Most of the world's nations have ratified the 1997 Kyoto Protocol on "greenhouse gas" emissions reduction (in force eight years come next Wednesday). We're trying to do our bit to "save the planet": as part of the UK's 2011 Carbon Plan and 2009 Renewable Energy Strategy the Government has initiated the Renewable Heat Incentive. This encourages the burning of waste as a way of providing heat as well as disposing of rubbish. Sounds good, and there happens to be recently-contructed incinerator only a couple of miles away from me, in south Birmingham.
But it's not purely beneficial, as the readers' letters pages in The Oldie magazine point out. In response to TV personality Johnny Ball's lately-expressed support for incinerators, Michael Ryan of Shrewsbury (January 2013 issue) used ONS data to suggest a link between incinerator emissions and increased infant mortality. In the February issue (just out), Chris Butler of Borough Green in Kent writes in to say that the Public Health Observatory blames atmospheric particulates for 5.6% of mortality in England. (That's not to say that all the particles come from incinerators; nor that we'd live forever if the air was clean. But this London website quotes the same PHO figure and says it's worse in London: 6 - 9% of mortality so attributable.)
Mr Butler makes a second reference in the same letter, this time to the DECC's own July 2012 impact assessment of the Renewable Heat Incentive. This attempts to quantify in monetary terms the pros and cons of (a) doing nothing about incinerators' emissions and (b) introducing stricter rules. If the sums are right, the cost of extra regulation discounted back to today would be £420 million, but the benefits in terms of better health and reduced mortality are estimated at nearly £3 billion. (How are exactly are these figures calculated? What happens if the discount rate used (3.5%) is higher or lower? One can imagine the money-debate rattling on.)
And it can be very hard to apply money to values. How do we price health and life per se, apart from the cost of medical interventions, social security costs for the sick and so on? What counts as the best solution depends so much on what kind of, and the degree to which, "negative externality" is internalized into the calculation, if at all. For example, one of the externalities not assessed in this report is the impact on the ecosystem (see paragraph 33).
And one option is simply not to care at all. Stalin's view on externality was brutally simple: no man, no problem.
Not all particulates are equally hazardous, but none is deemed safe: "the World Health Organisation advise that there is no safe exposure level to P(articulate) M(atter)," says the DECC's report. The danger is not uniform in time, either, e.g. more dioxins are emitted at operational startup and shutdown than in mid-burn.
The damage caused by other pollutants is not yet completely known, and there are many of them: "Incinerator emissions are a major source of fine particulates, of toxic metals and of more than 200 organic chemicals, including known carcinogens, mutagens, and hormone disrupters," says this 2008 report by the British Society for Ecological Medicine. Perhaps the chemtrail conspiracy-hunters should turn their attention from the skies to their local waste tip.
What are the facts, then, and what are the relevant facts, and what values should we use in relation to them? There's so much uncertainty and room for disagreement that the precautionary principle might save us much ill-tempered controversy as well as, possibly, harm to life and health: let's simply make less waste in the first place.
Now to put out two large bags of washed plastic bottles, for tomorrow's binmen.
Nothing here should be taken as personal advice, financial or otherwise. No liability is accepted for third-party content, whether incorporated in or linked to this blog; or for unintentional error and inaccuracy. The blog author may have, or intend to change, a personal position in any stock or other kind of investment mentioned.
What Lessons From Germany and Denmark? [2]
If the Danish electricity sector is an unrepresentative model for most other nations to follow, by dint of its hard-to-replicate access to ultra-flexible hydro electricity from Norway, the Danes do at least seem to have a feasible (if expensive) structure in place. The same cannot be said of Germany, that other favourite exemplar of red/green advocates of renewable energy, which upon examination is a very odd model for them to be eulogising.
To summarise: Germany barely got through 2012 without serious blackouts; voltage has become highly unreliable in many parts of their complex grid system; heavily subsidised renewables have trashed the German wholesale power market; neighbouring markets are also suffering as a result of unpredictable surges of German wind-power exports; Germany is building a large number of big new coal- and lignite-fired power stations to cope; in the interim, they have become dependent on large-scale imports from some very dirty old lignite plants in Eastern Europe; and to crown it all, their CO2 emissions are increasing!
How has this come to pass?
On major issues like energy, German policy is generally framed by big, set-piece legislation that lays down what is in effect a national plan. The last coherent German energy plan dates back to the 1980s, and more recent policies have been layered on top in an ad hoc fashion. That's how it's often done in the UK and other countries, but for methodical Germany it is anomalous: and intelligent Germans view the resultant mess as inevitable.
The most recent nonsense was the sequence of on-off-on-off nuclear decisions, culminating in a post-Fukushima bombshell: the summary closure of a large part of the nuclear fleet. This was always going to leave a big gap to fill in a hurry - hence the immediate increase in imports, which naturally come from neighbours with surplus capacity: France (nuclear, of course), Poland and the Czech Republic (coal, some of it dreadfully polluting lignite). The ironies are obvious, and one hopes the anti-nuke greens are proud of themselves.
But the subtler and even less tractable issue is the unforeseen impact of large amounts of 'must take' wind- and solar-power, financed by whopping subsidies. (The electricity doesn't even need to be generated - the producer merely needs to install the plant. There are many windfarms in northern Germany that are completed but not connected to the grid - the system cannot accommodate them, and they lie idle - getting paid anyway.)
Key to the situation is that the marginal cost of wind- and solar-power is close to zero. Unsurprisingly, at times of the day when large quantities of zero-cost power are being fed into the grid (foisted on utilities who must take it, irrespective of its market value), the impact on the wholesale market price is to reduce it substantially - not just to zero, it sometimes actually goes negative, so that people are being paid to take power off the system
The timing of wind generation is notoriously unpredictable, but solar is straightforward: it peaks around noon. In Germany (though not in all countries) this at least coincides with peak demand. The impact on wholesale prices is clear.
One cannot fail to notice (a) demand rising to maximum at midday ('Volume' on the chart) which would 'normally' coincide with the highest hourly prices: but (b) a midday collapse in hourly price, which at 1pm is lower than at midnight ! The market price for 'peak' electricity as defined in the German/Austrian market (9 am to 8 pm) is now barely greater than for baseload (24-hour), meaning inter alia that no-one will see any incentive to build or run a plant designed to offer flexibility. In particular, it fundamentally undermines the economics of flexible gas-fired plant, which - since no subsidies are on offer to fossil fuels - needs a 'normal', undistorted day-time price to pay its way. And yet that is the very plant needed to balance the vagaries of wind generation !
Why this was not foreseen is a matter for conjecture. (Personally, I reckon - and have offered evidence elsewhere - that many Germans who should know better genuinely do not understand how markets work.) But of this we may be sure: its impact is highly destabilising.
READ ON:
PART THREE
PART FOUR (CONCLUSION)
PREVIOUS: PART ONE
Nothing here should be taken as personal advice, financial or otherwise. No liability is accepted for third-party content, whether incorporated in or linked to this blog; or for unintentional error and inaccuracy. The blog author may have, or intend to change, a personal position in any stock or other kind of investment mentioned.
To summarise: Germany barely got through 2012 without serious blackouts; voltage has become highly unreliable in many parts of their complex grid system; heavily subsidised renewables have trashed the German wholesale power market; neighbouring markets are also suffering as a result of unpredictable surges of German wind-power exports; Germany is building a large number of big new coal- and lignite-fired power stations to cope; in the interim, they have become dependent on large-scale imports from some very dirty old lignite plants in Eastern Europe; and to crown it all, their CO2 emissions are increasing!
How has this come to pass?
On major issues like energy, German policy is generally framed by big, set-piece legislation that lays down what is in effect a national plan. The last coherent German energy plan dates back to the 1980s, and more recent policies have been layered on top in an ad hoc fashion. That's how it's often done in the UK and other countries, but for methodical Germany it is anomalous: and intelligent Germans view the resultant mess as inevitable.
The most recent nonsense was the sequence of on-off-on-off nuclear decisions, culminating in a post-Fukushima bombshell: the summary closure of a large part of the nuclear fleet. This was always going to leave a big gap to fill in a hurry - hence the immediate increase in imports, which naturally come from neighbours with surplus capacity: France (nuclear, of course), Poland and the Czech Republic (coal, some of it dreadfully polluting lignite). The ironies are obvious, and one hopes the anti-nuke greens are proud of themselves.
But the subtler and even less tractable issue is the unforeseen impact of large amounts of 'must take' wind- and solar-power, financed by whopping subsidies. (The electricity doesn't even need to be generated - the producer merely needs to install the plant. There are many windfarms in northern Germany that are completed but not connected to the grid - the system cannot accommodate them, and they lie idle - getting paid anyway.)
Key to the situation is that the marginal cost of wind- and solar-power is close to zero. Unsurprisingly, at times of the day when large quantities of zero-cost power are being fed into the grid (foisted on utilities who must take it, irrespective of its market value), the impact on the wholesale market price is to reduce it substantially - not just to zero, it sometimes actually goes negative, so that people are being paid to take power off the system
The timing of wind generation is notoriously unpredictable, but solar is straightforward: it peaks around noon. In Germany (though not in all countries) this at least coincides with peak demand. The impact on wholesale prices is clear.
 |
| Source: EPEX |
Why this was not foreseen is a matter for conjecture. (Personally, I reckon - and have offered evidence elsewhere - that many Germans who should know better genuinely do not understand how markets work.) But of this we may be sure: its impact is highly destabilising.
READ ON:
PART THREE
PART FOUR (CONCLUSION)
PREVIOUS: PART ONE
Nothing here should be taken as personal advice, financial or otherwise. No liability is accepted for third-party content, whether incorporated in or linked to this blog; or for unintentional error and inaccuracy. The blog author may have, or intend to change, a personal position in any stock or other kind of investment mentioned.
Sunday, January 06, 2013
What Lessons from Germany and Denmark? [1]
Energy, like defence, is a topic where huge numbers of people seem to have strong views based on very little knowledge. If evidence is required, go to the Guardian’s Comment is Free website where almost any piece on an energy topic receives hundreds of comments exhibiting ignorance aplenty.
A favourite theme from the green/red camp is ‘what about Germany?’ or its close variant ‘if Denmark can do it, we can, too’. The ‘it’ in question is of course very large-scale renewable generation in both countries, which is taken to be triumphantly proving its worth there in quantities that put the UK to shame.
At the headline level, the statistics are striking. In the 1st half of 2012, renewables generated around 25% of Germany’s electricity, of which 9% was wind and 5% solar. (The balance is mostly biofuels, which greens are a bit more ambivalent about, but let that pass.) Denmark has reached 24% of electricity consumption being generated from renewables: and as a percentage of Denmark’s own generation, the figures are even more remarkable: over 40% is renewable, of which 28% is wind.
The difference between Denmark’s ‘24% of consumption’ and ‘40% of own generation’ immediately tips us off to an important additional factor – imports, or, more generally, cross-border electricity trade. Trade between interconnected countries is generally in either direction at different times, as advocates of free trade would hope and expect: wholesale electricity prices in one country will rarely be identical to those in a neighbour’s market, given different supply/demand dynamics, generation fleets, weather etc. Cross-border trade is the highly appropriate result.
In Denmark’s case the detailed pattern is complex: they do indeed export electricity some of the time but, as the figures suggest, they are generally substantial net importers. Wind turbines, of course, produce ‘intermittently’ (and relatively unpredictably): and anyone wishing to hold up Denmark’s renewables as an example for other nations should be aware that their significant amount of wind generation is only feasible because of the ease with which they are able to import the ultra-flexible hydro-power available from Norway. Attempting to balance the grid using their remaining indigenous sources - the largest of which is, yes, coal - would not be remotely economic, and in fact would probably not be feasible at any price (we will comment later on cost aspects.)
Wind plus hydro can be a feasible combination with which to satisfy electricity demand. Denmark, where this is achievable, doesn’t offer a model for countries where there is little or no hydro on tap (or, of course, some equally flexible alternative - of which there are very few indeed).
Germany’s import / export pattern is exceptionally complex, and changing all the time as the unexpected post-Fukushima decision, to shut down a significant portion of its nuclear capacity, is accommodated. But it is not hydro imports that make Germany an unconvincing model for other nations. Rather, it is the distinct possibility that Germany’s power system is not feasible at all.
Read on:
PART TWO
PART THREE
PART FOUR (CONCLUSION)
Nothing here should be taken as personal advice, financial or otherwise. No liability is accepted for third-party content, whether incorporated in or linked to this blog; or for unintentional error and inaccuracy. The blog author may have, or intend to change, a personal position in any stock or other kind of investment mentioned.
A favourite theme from the green/red camp is ‘what about Germany?’ or its close variant ‘if Denmark can do it, we can, too’. The ‘it’ in question is of course very large-scale renewable generation in both countries, which is taken to be triumphantly proving its worth there in quantities that put the UK to shame.
At the headline level, the statistics are striking. In the 1st half of 2012, renewables generated around 25% of Germany’s electricity, of which 9% was wind and 5% solar. (The balance is mostly biofuels, which greens are a bit more ambivalent about, but let that pass.) Denmark has reached 24% of electricity consumption being generated from renewables: and as a percentage of Denmark’s own generation, the figures are even more remarkable: over 40% is renewable, of which 28% is wind.
The difference between Denmark’s ‘24% of consumption’ and ‘40% of own generation’ immediately tips us off to an important additional factor – imports, or, more generally, cross-border electricity trade. Trade between interconnected countries is generally in either direction at different times, as advocates of free trade would hope and expect: wholesale electricity prices in one country will rarely be identical to those in a neighbour’s market, given different supply/demand dynamics, generation fleets, weather etc. Cross-border trade is the highly appropriate result.
In Denmark’s case the detailed pattern is complex: they do indeed export electricity some of the time but, as the figures suggest, they are generally substantial net importers. Wind turbines, of course, produce ‘intermittently’ (and relatively unpredictably): and anyone wishing to hold up Denmark’s renewables as an example for other nations should be aware that their significant amount of wind generation is only feasible because of the ease with which they are able to import the ultra-flexible hydro-power available from Norway. Attempting to balance the grid using their remaining indigenous sources - the largest of which is, yes, coal - would not be remotely economic, and in fact would probably not be feasible at any price (we will comment later on cost aspects.)
Wind plus hydro can be a feasible combination with which to satisfy electricity demand. Denmark, where this is achievable, doesn’t offer a model for countries where there is little or no hydro on tap (or, of course, some equally flexible alternative - of which there are very few indeed).
Germany’s import / export pattern is exceptionally complex, and changing all the time as the unexpected post-Fukushima decision, to shut down a significant portion of its nuclear capacity, is accommodated. But it is not hydro imports that make Germany an unconvincing model for other nations. Rather, it is the distinct possibility that Germany’s power system is not feasible at all.
Read on:
PART TWO
PART THREE
PART FOUR (CONCLUSION)
Nothing here should be taken as personal advice, financial or otherwise. No liability is accepted for third-party content, whether incorporated in or linked to this blog; or for unintentional error and inaccuracy. The blog author may have, or intend to change, a personal position in any stock or other kind of investment mentioned.
Max Keiser and George Galloway: a deafening silence in the media
On 20th November, Max Keiser addressed a large audience in the Grand Committee Room in the Houses of Parliament, as the guest of George Galloway MP.
Galloway pointed out that this was the second largest public room in Parliament (the first had already been booked) and all MPs had been invited in writing, twice - yet none of them had turned up.
In some ways this is understandable: Galloway is "colourful" and, to me, something of an enigma, and his fellow Parliamentarians must have considered the risk of tainting by association.
Or worse, reputational entrapment: for although Keiser had strong criticisms to make of Gordon Brown's gold sale (1999 - 2002), which he said is the moment when Britain's independence was surrendered, he also laid the blame for the present crisis on the monetary expansion that began under Reagan and Thatcher. Additionally, he had harsh words to say about George Osborne and David Cameron, whom he sees as fighting for corrupt City interests. In the circumstances, MPs on both sides must have seen little political advantage in attending.
Yet there wasn't that much else on in Parliament on the evening of 20th November. The House of Commons Order of Business after 7 p.m. was a handful of decisions to be made without debate, plus the presentation of a petition and the Adjournment Debate. Granted, many MPs would be heading home for the weekend - but another hour or so, of worthwhile economic instruction, might have done them some good.
And it's surprising that, try as I may, I can find no mainstream media report of Keiser's speech. Remember that he is possibly the most-watched TV journalist in the world, talking on a subject of the utmost importance in the very heart of London. This, perhaps deliberate neglect plays into the growing public cynicism about our political elite and the Fourth Estate.
Regular Keiser-watchers will have heard much of his material before, many times, though it may be news to some that the reason he's shifted his base of operations to London is that he wants a ringside seat to cover what he sees as the coming, full-blown disaster of historic proportions, and expects our poor country to be the epicentre.
He also says that Germany will use its gold hoard and massive Eurobond issuance to establish its advantage over the City; Frankfurt will become the centre of banking and trading in Europe, he feels. Britain, having allowed its financial sector to swell to over 10% of national GDP, has set itself up for a terrible fall.
According to Keiser, only raising interest rates sharply - as Paul Volcker did in the USA (20% by 1981) - can cleanse the speculation and malpractice from the system; and he doesn't see us doing that.
Also interesting in this film, is the naivety of questions, underlining Keiser's (and George Osborne's) observations about the financial illiteracy of the British public.
Like Nigel Farage (another ex-financial trader), Keiser is loud, brash and fast-talking (he starts more sentences than he finishes); and both are also, in my assessment, completely sincere in their concern and indignation.
The film lasts slightly more than an hour, but you can simply listen to it while doing something else, as I did. I think you'll find it worth your while.
Nothing here should be taken as personal advice, financial or otherwise. No liability is accepted for third-party content, whether incorporated in or linked to this blog; or for unintentional error and inaccuracy. The blog author may have, or intend to change, a personal position in any stock or other kind of investment mentioned.
Galloway pointed out that this was the second largest public room in Parliament (the first had already been booked) and all MPs had been invited in writing, twice - yet none of them had turned up.
In some ways this is understandable: Galloway is "colourful" and, to me, something of an enigma, and his fellow Parliamentarians must have considered the risk of tainting by association.
Or worse, reputational entrapment: for although Keiser had strong criticisms to make of Gordon Brown's gold sale (1999 - 2002), which he said is the moment when Britain's independence was surrendered, he also laid the blame for the present crisis on the monetary expansion that began under Reagan and Thatcher. Additionally, he had harsh words to say about George Osborne and David Cameron, whom he sees as fighting for corrupt City interests. In the circumstances, MPs on both sides must have seen little political advantage in attending.
Yet there wasn't that much else on in Parliament on the evening of 20th November. The House of Commons Order of Business after 7 p.m. was a handful of decisions to be made without debate, plus the presentation of a petition and the Adjournment Debate. Granted, many MPs would be heading home for the weekend - but another hour or so, of worthwhile economic instruction, might have done them some good.
And it's surprising that, try as I may, I can find no mainstream media report of Keiser's speech. Remember that he is possibly the most-watched TV journalist in the world, talking on a subject of the utmost importance in the very heart of London. This, perhaps deliberate neglect plays into the growing public cynicism about our political elite and the Fourth Estate.
Regular Keiser-watchers will have heard much of his material before, many times, though it may be news to some that the reason he's shifted his base of operations to London is that he wants a ringside seat to cover what he sees as the coming, full-blown disaster of historic proportions, and expects our poor country to be the epicentre.
He also says that Germany will use its gold hoard and massive Eurobond issuance to establish its advantage over the City; Frankfurt will become the centre of banking and trading in Europe, he feels. Britain, having allowed its financial sector to swell to over 10% of national GDP, has set itself up for a terrible fall.
According to Keiser, only raising interest rates sharply - as Paul Volcker did in the USA (20% by 1981) - can cleanse the speculation and malpractice from the system; and he doesn't see us doing that.
Also interesting in this film, is the naivety of questions, underlining Keiser's (and George Osborne's) observations about the financial illiteracy of the British public.
Like Nigel Farage (another ex-financial trader), Keiser is loud, brash and fast-talking (he starts more sentences than he finishes); and both are also, in my assessment, completely sincere in their concern and indignation.
The film lasts slightly more than an hour, but you can simply listen to it while doing something else, as I did. I think you'll find it worth your while.
Nothing here should be taken as personal advice, financial or otherwise. No liability is accepted for third-party content, whether incorporated in or linked to this blog; or for unintentional error and inaccuracy. The blog author may have, or intend to change, a personal position in any stock or other kind of investment mentioned.
Saturday, January 05, 2013
Looking for a widget!
Help wanted! We thought we'd found a multiple blog widget so you can follow all pages in one simple device, but the one we got can't be installed by readers. Anyone out there know a good one?
Friday, January 04, 2013
Airbrushing out The Queen
My wife asked me what this was, on the back of a pound coin:
... and on further investigation it seems that ever since this little metal thing was introduced into our system of exchange, the Royal Arms have been omitted (except for the 1988 design) in favour of a cycle of images from the regions.
Doubtless we'll be told not to take it too seriously, but it seems to me that the 1.5 billion pound coins are being used as yet another method to condition us to accept the "inevitable" breakup of the Union.
Another subliminal point, maintains the wife of a friend, is that the change from a banknote to a small coin was to help us not to expect so much for our money.
Nothing here should be taken as personal advice, financial or otherwise. No liability is accepted for third-party content, whether incorporated in or linked to this blog; or for unintentional error and inaccuracy. The blog author may have, or intend to change, a personal position in any stock or other kind of investment mentioned.
It's the Arms of the City of London:
... and on further investigation it seems that ever since this little metal thing was introduced into our system of exchange, the Royal Arms have been omitted (except for the 1988 design) in favour of a cycle of images from the regions.
Doubtless we'll be told not to take it too seriously, but it seems to me that the 1.5 billion pound coins are being used as yet another method to condition us to accept the "inevitable" breakup of the Union.
Another subliminal point, maintains the wife of a friend, is that the change from a banknote to a small coin was to help us not to expect so much for our money.
Nothing here should be taken as personal advice, financial or otherwise. No liability is accepted for third-party content, whether incorporated in or linked to this blog; or for unintentional error and inaccuracy. The blog author may have, or intend to change, a personal position in any stock or other kind of investment mentioned.
Thursday, January 03, 2013
Nick Drew: Solar power the worst option for reducing carbon emissions
See The Energy Page for an industry expert's assessment.
Nothing here should be taken as personal advice, financial or otherwise. No liability is accepted for third-party content, whether incorporated in or linked to this blog; or for unintentional error and inaccuracy. The blog author may have, or intend to change, a personal position in any stock or other kind of investment mentioned.
Nothing here should be taken as personal advice, financial or otherwise. No liability is accepted for third-party content, whether incorporated in or linked to this blog; or for unintentional error and inaccuracy. The blog author may have, or intend to change, a personal position in any stock or other kind of investment mentioned.
Nick Drew: Solar fad a waste of money
Energy expert and journalist Nick Drew has written a new piece for The Energy Page on cost-effective ways to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. Turns out that the fashion for roof-mounted solar panels is just about the worst possible option - read the full story here.
Nick is a regular contributor to the Capitalists@Work blog.
************
Nothing here should be taken as personal advice, financial or otherwise. No liability is accepted for third-party content, whether incorporated in or linked to this blog; or for unintentional error and inaccuracy. The blog author may have, or intend to change, a personal position in any stock or other kind of investment mentioned.
Solar Power is Daylight Robbery
The UK government is very fond of claiming that its decarbonisation policy is being delivered at least cost to UK citizens. Irrespective of whether one supports the policy goal, one would at least like to believe them on the cost.
Sadly, their claim is a blatant falsehood; and we can see why this is by utilizing the government's own methodologies.
A very standard way of presenting the cost-effectiveness of measures that can reduce CO2 emissions is the Marginal Abatement Cost Curve (MACC) and we will look at some examples below. The basic concept is simple: for each measure, calculate the cost per unit of CO2 emissions reduced, and rank them from cheapest to most expensive on a bar-chart. If we pick (e.g.) a particular market segment, we can additionally plot the total absolute potential for CO2 abatement each measure can deliver in that sector (e.g. in tonnes), by making the width of each bar correspond to the amount.
Having ranked them thus, for a given target amount of reductions we can directly read off the cost of the most expensive measure required to achieve the target. And why would anyone institute measures that cost more than absolutely necessary ? Surely, they would exhaust the potential of the cheapest measures first, before proceeding to the more expensive.
Before looking at UK examples, it is interesting to note that in every MACC example one ever sees, the cheapest abatement measures are in fact profitable - that is, they pay for themselves - in some cases, handsomely so: their 'cost' is not just cheap, it is negative. (We will consider what this means in policy terms another time.) Our first example shows this aspect clearly: it comes from DECC and is the MACC of the total potential abatement identified in the UK 'non-traded' sector (the part of the economy not subject to the EU Emissions Trading Scheme), for the period 2023–27.
As can be seen, at the left-hand side there is around 90 MtCO2e abatement potential that pays for itself. We should only need to start paying for abatement if the target was in excess of that amount. The weighted average of the cost (by a complex calculation) is £43 per tonne, which coincides with an abatement potential of around 130 Mt - well over half the total. Even the most expensive measures plotted come in at under £250 per tonne.
This, then, is a baseline of sorts, and certainly gives some background perspective for considering the next chart, which is the detailed MACC for abatement potential in the UK residential sector through to 2020.
Note that solar power (PV generation) is well to the right of the curve, with a cost that towers over most of the measures available. (Solar water-heating is even worse.) Secondly, at £265 per tonne it is more expensive than any of the measures from the previous MACC.
A very obvious conclusion must surely be that solar power should not be receiving public money (via whatever mechanism) until the vastly greater potential that is available at very much less cost has been comprehensively exploited. Needless to say, the opposite is the case: residential solar power installations are heavily subsidized via our electricity bills, while huge amounts of cheaper - much cheaper - abatement potential lies dormant.
No end of sophistry is offered to defend this state of affairs. Costs of PV are falling all the time; many jobs have been created (mostly in China, of course); we need to create a level playing-field for all technologies (whatever that means). And there are all manner of nuances relating to the interpretation of MACCs - as DECC is keen to tell us (Box B5 here).
No amount of ratiocination, however, can deflect the accusation that subsidizing solar PV in the UK is indefensible from a cost perspective. And in straightened times, costs matter.
Nothing here should be taken as personal advice, financial or otherwise. No liability is accepted for third-party content, whether incorporated in or linked to this blog; or for unintentional error and inaccuracy. The blog author may have, or intend to change, a personal position in any stock or other kind of investment mentioned.
Sadly, their claim is a blatant falsehood; and we can see why this is by utilizing the government's own methodologies.
A very standard way of presenting the cost-effectiveness of measures that can reduce CO2 emissions is the Marginal Abatement Cost Curve (MACC) and we will look at some examples below. The basic concept is simple: for each measure, calculate the cost per unit of CO2 emissions reduced, and rank them from cheapest to most expensive on a bar-chart. If we pick (e.g.) a particular market segment, we can additionally plot the total absolute potential for CO2 abatement each measure can deliver in that sector (e.g. in tonnes), by making the width of each bar correspond to the amount.
Having ranked them thus, for a given target amount of reductions we can directly read off the cost of the most expensive measure required to achieve the target. And why would anyone institute measures that cost more than absolutely necessary ? Surely, they would exhaust the potential of the cheapest measures first, before proceeding to the more expensive.
Before looking at UK examples, it is interesting to note that in every MACC example one ever sees, the cheapest abatement measures are in fact profitable - that is, they pay for themselves - in some cases, handsomely so: their 'cost' is not just cheap, it is negative. (We will consider what this means in policy terms another time.) Our first example shows this aspect clearly: it comes from DECC and is the MACC of the total potential abatement identified in the UK 'non-traded' sector (the part of the economy not subject to the EU Emissions Trading Scheme), for the period 2023–27.
 |
| Source: DECC |
This, then, is a baseline of sorts, and certainly gives some background perspective for considering the next chart, which is the detailed MACC for abatement potential in the UK residential sector through to 2020.
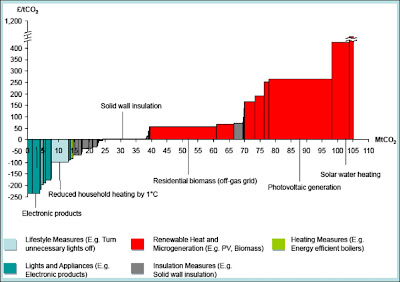 |
| Source: Committee on Climate Change |
A very obvious conclusion must surely be that solar power should not be receiving public money (via whatever mechanism) until the vastly greater potential that is available at very much less cost has been comprehensively exploited. Needless to say, the opposite is the case: residential solar power installations are heavily subsidized via our electricity bills, while huge amounts of cheaper - much cheaper - abatement potential lies dormant.
No end of sophistry is offered to defend this state of affairs. Costs of PV are falling all the time; many jobs have been created (mostly in China, of course); we need to create a level playing-field for all technologies (whatever that means). And there are all manner of nuances relating to the interpretation of MACCs - as DECC is keen to tell us (Box B5 here).
No amount of ratiocination, however, can deflect the accusation that subsidizing solar PV in the UK is indefensible from a cost perspective. And in straightened times, costs matter.
* * * * *
Nothing here should be taken as personal advice, financial or otherwise. No liability is accepted for third-party content, whether incorporated in or linked to this blog; or for unintentional error and inaccuracy. The blog author may have, or intend to change, a personal position in any stock or other kind of investment mentioned.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)


